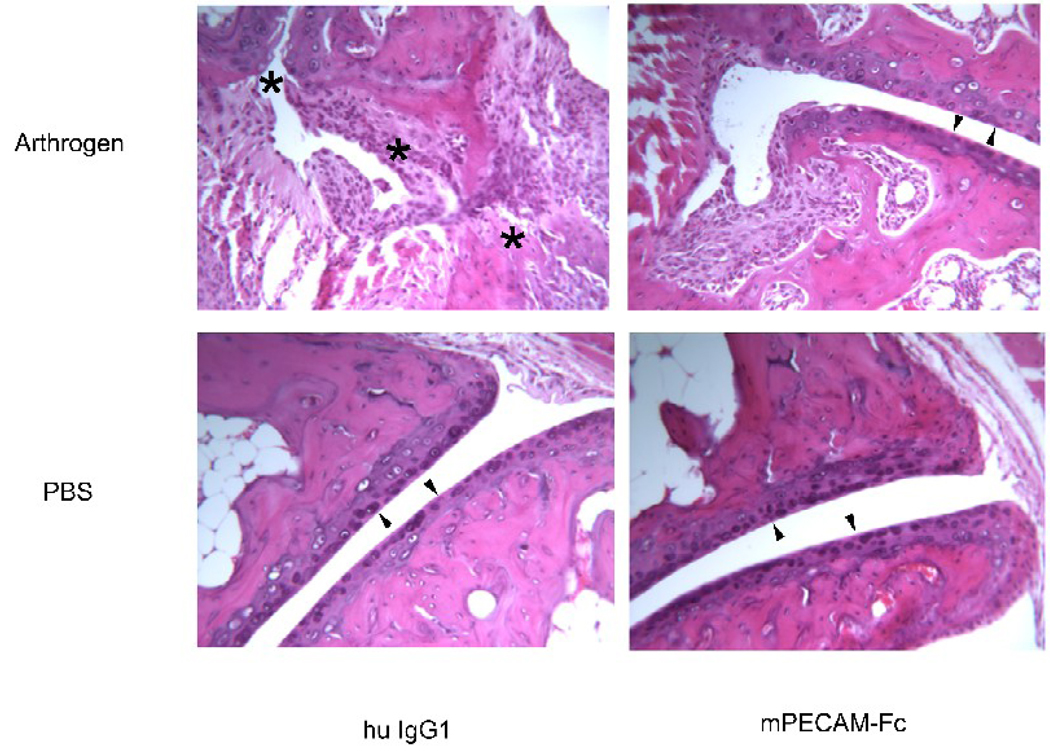
Figure 4. Soluble PECAM chimera protects from bone destruction in CAIA.
Representative histopathology of hind joints. The same portion of the joint is shown in each panel. Minimal synovial hyperplasia or leukocyte infiltration is seen in the mice that did not receive arthrogen (bottom two panels). Note smooth articular cartilage surfaces (arrowheads). Mice that received arthrogen and were treated with control human IgG1 showed significant synovial hyperplasia, pannus formation and numerous infiltrating leukocytes (upper left panel). There was significant bone and cartilage destruction and disruption of the articular surface of the joint (asterisks along what used to be joint space). In contrast, mice that received arthrogen and were subsequently treated with PECAM-Fc showed markedly reduced leukocyte infiltration and synovial hyperplasia. Note preserved articular surface (arrowhead). There was also an absence of cartilage erosion or bone destruction, and the articular surfaces of the joint appear intact and smooth (upper right panel). Pictures are representative of all mice in each treatment group from all experiments. Original magnification = 125×.