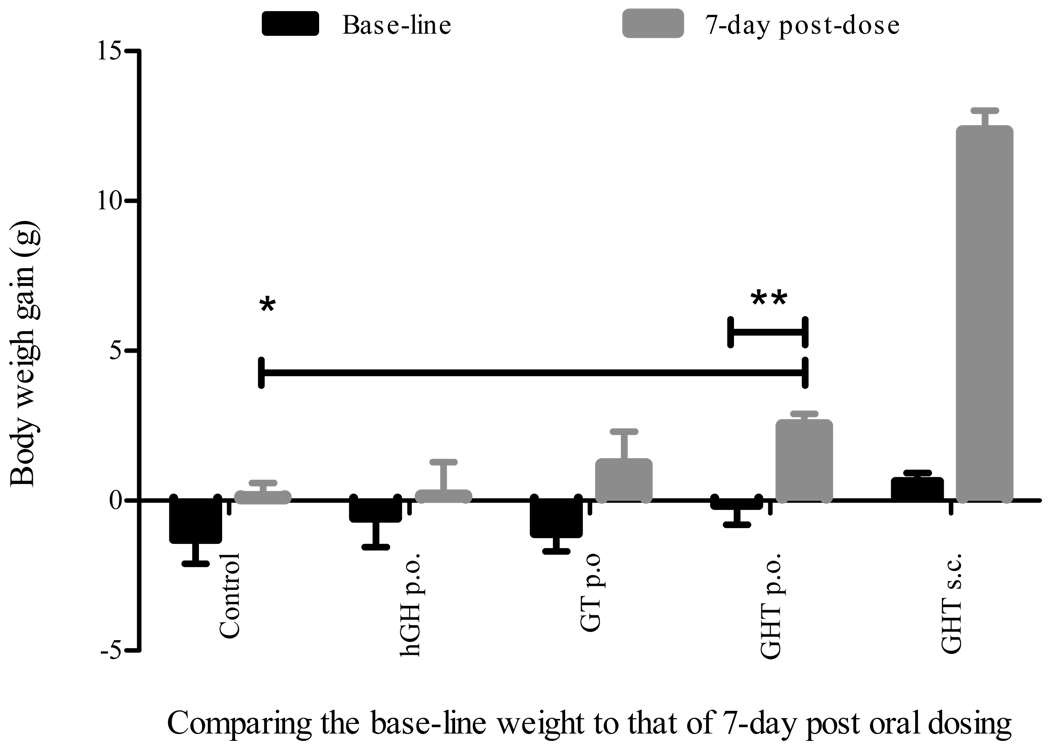
Fig. 5.
Oral administration of the GHT fusion protein led to body weight gain. Body weight of the hypophysectomized rats were monitored for 7-days and the base-line weight were established for five experimental groups. The fasted rats were orally administered (p.o.) with GHT fusion protein (12.5 mg/kg), GT fusion protein (12.5 mg/kg), hGH (2.5 mg/kg), and vehicle control for 7-consecutive days, respectively, and one group of rats were given GHT fusion protein s.c. as a positive control. The body weight gain was determined by subtracting the weight on the day of dosing (day 1) from that of one day after last dosing (day 8), and then compared to that of base-line weight. Data represent mean of body weight gain ± SEM (n = 5, except GHT s.c. where n = 4 and vehicle control where n = 3). The two-tailed t-test showed that the differences of base line weight gain versus oral GHT weight gain and of the vehicle control versus oral GHT weight gain were both statistically significant (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.01). However, the difference between base line weight versus 7-day oral dosing with GT, hGH, or control was not significant (p > 0.1).