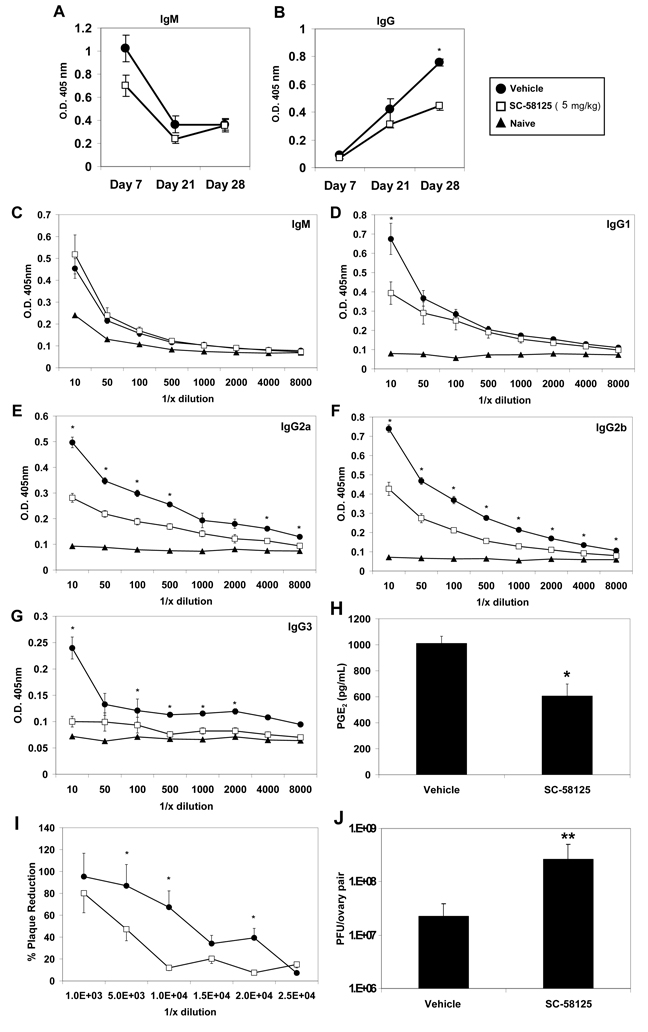
Figure 3.
Chronic exposure to the Cox-2 inhibitor, SC-58125, impairs production of VV-specific neutralizing IgG. C57BL/6 mice (n = 4) were administered vehicle or SC-58125 (5 mg/kg) starting seven days before infection with VV (1×106 PFU) and ending on day 27. Plasma collected from vehicle treated (closed circles) or SC-58125 treated (open squares) mice on days 7, 21 and 28 was analyzed for VV-specific IgM (A) and IgG (B). VV-specific IgM (C), IgG1 (D), IgG2a (E), IgG2b (F) or IgG3 (G) titers were more extensively characterized by ELISA from day 28 plasma samples. (H) Splenocytes harvested 7 days post-infection were cultured with 10 ug/mL LPS for 24 hours and supernatants were assessed for PGE2 production by EIA. (I) The presence of neutralizing antibody titers in mouse plasma was assessed by plaque assay. VV was incubated with dilutions (10−2, 5−2, 10−3, 15−3, 20−3, 25−3) of vehicle treated or SC-58125 treated mouse plasma and cultured with 143B fibroblasts. The percent reduction of plaques in the presence of plasma compared to no plasma controls is shown. (J) Ovarian viral titers were determined on day 7 post-infection in mice chronically treated with vehicle or SC-58125. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, * p <0.05, **p = 0.06.