Fig. 3.
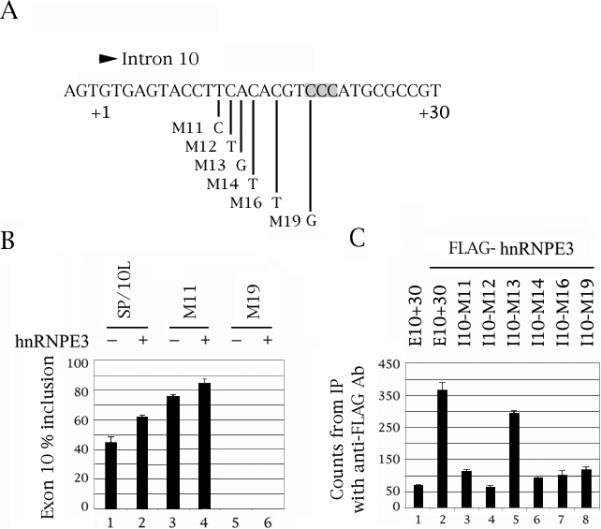
Mutation of C residue +19 of the intron downstream of tau exon 10, which affects an intronic enhancer, abolishes hnRNPE3 action and binding. (A) The last three nucleotides of exon 10 and nucleotides +1 to +30 of the intron downstream of tau exon 10. The point mutations are indicated. The C triplet that is the likely site of the hnRNPE3 interaction is shaded. (B) RT-PCR of wild-type and point-mutated SP/10L in COS cells in the absence and presence of hnRNPE3. The RT-PCR products come from 1:1 co-transfections of tau constructs and FLAG-hnRNPE3. Co-transfections were not done with mutants M12-16, because they exhibit 100% exon 10 inclusion and would not show additional activation by hnRNPE3. Primers and graph conventions are as in Fig.1C. (C) 32P-labeled riboprobes containing wild-type or point-mutated exon 10 were incubated with extracts from COS cells transfected with FLAG-hnRNPE3 and were immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody M2. Amounts of riboprobe bound to the hnRNPE3 protein were calculated relative to the nonspecific binding of the FLAG vector transfection by measuring the counts retained after washing (means ± SD of three analyses). Equal amounts of FLAG- hnRNPE3 were present in each experiment.
