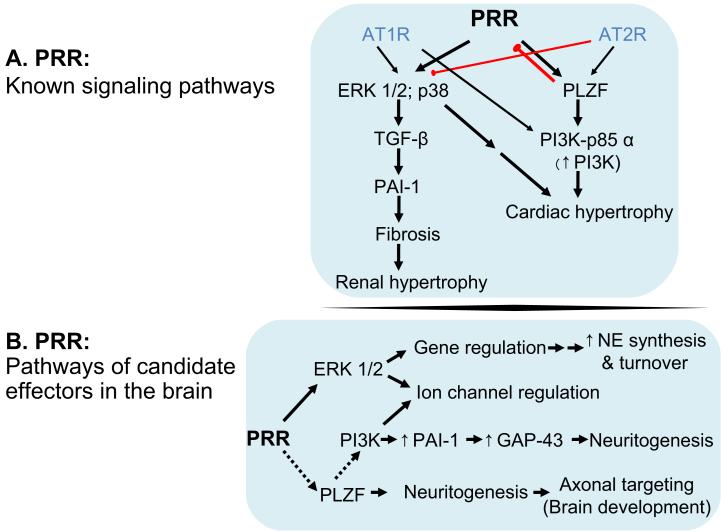
Figure 2.
Downstream signaling by the PRR and role of potential effectors in brain neurons. Top, Activation of PRR by renin or prorenin activates MAP kinases such as ERK 1/2 in the kidney, smooth muscle cells and in brain neurons as well as p38 in the heart. MAP kinase activation by PRR activates TGF-β to promote PAI-1secretion, which leads to fibrosis. In addition PRR stimulates the transcription factor PLZF, which mediates upregulation of the PI3 kinase adaptor protein p85α that promotes PI3-kinase activity. Bottom, Of the potential downstream effector of PRR, in the brain, only ERK 1/2 has been demonstrated, thus far. ERK 1/2, itself mediates gene regulation that include upregulation of enzymes and transporter proteins that promote norepinephrine turnover. ERK 1/2 is also found to modulate K+ channel function. Future studies may show that PRR is linked PLZF function to mediate neuronal maturation in the brain. PLZF is present in various regions of the brain where it is important for neuronal organization. PI3-kinase function, linked to PLZF action can further link PRR to channel regulation, in addition, promoting neurite growth. These actions are linked to tissue hypertrophy and end organ failure and also mediate neurogenic hypertension. Black Arrows, established signal transduction pathways; red arrow, inhibitory pathways; dotted lines, candidate pathways.