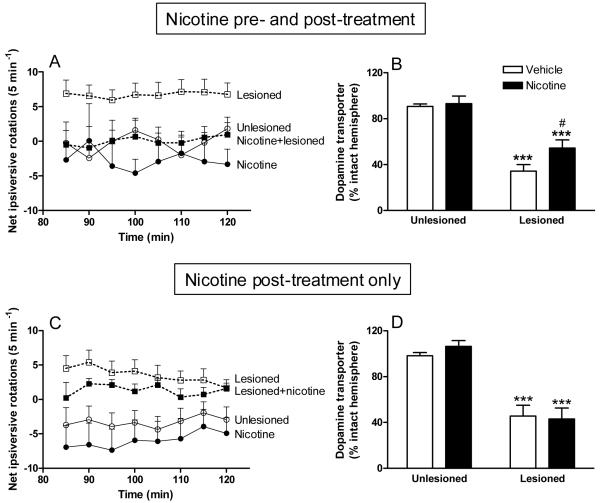
Fig. 1. Nicotine exposure is neuroprotective against ongoing nigrostriatal damage, but not neurorestorative in rats.
In the top panels (A, B), nicotine (50 μg/ml) was administered to unlesioned rats in saccharin-containing drinking water, as previously described [41]. Two weeks later, the rats received intracranial injections of 6-OHDA or vehicle into the right medial forebrain bundle. To assess the effect of nicotine treatment on motor deficits that arise with nigrostriatal damage, amphetamine-induced ipsiversive rotation was assessed 2-3 weeks after lesioning, with the nicotine [41]. The rats were placed in the chamber for 30 min for acclimatization, after which amphetamine (4.0 mg/kg ip) was administered. Circling behavior was assessed between 85 to 120 min after amphetamine administration when effects of nicotine on circling had returned to control levels. The rats were then killed and dopamine transporter levels measured using autoradiography. This treatment regimen resulted in an improvement in aberrant motor behavior and in striatal dopamine transporter levels. In the nicotine post-treatment only study (C, D), rats were first lesioned with 6-OHDA, as described above. Two to 3 weeks later, nicotine (50 μg/ml) treatment was initiated and maintained throughout. Ipsiversive rotation was evaluated after 3-4 weeks on nicotine. The rats were then killed and dopamine transporter levels evaluated. By contrast, there was no improvement in aberrant turning behavior or striatal dopamine transporter levels when nicotine was administered after nigrostriatal damage was complete. Results are the mean ± SEM of 6-9 rats per group. With nicotine pre-treatment (A), there was a significant (p < 0.001) main effect of 6-OHDA lesioning on rotations assessed using three-way ANOVA and a significant (p < 0.05) interaction between nicotine treatment and 6-OHDA lesioning. By contrast, nicotine post-treatment (C) yielded a significant main effect of 6-OHDA lesioning (p < 0.001) but no interaction, by three-way ANOVA, suggesting no neuroprotection. Significance of difference from unlesioned group (B,D) using two-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test; ***p < 0.001, from lesioned #p < 0.05. Reproduced in modified form with permission from reference [41].