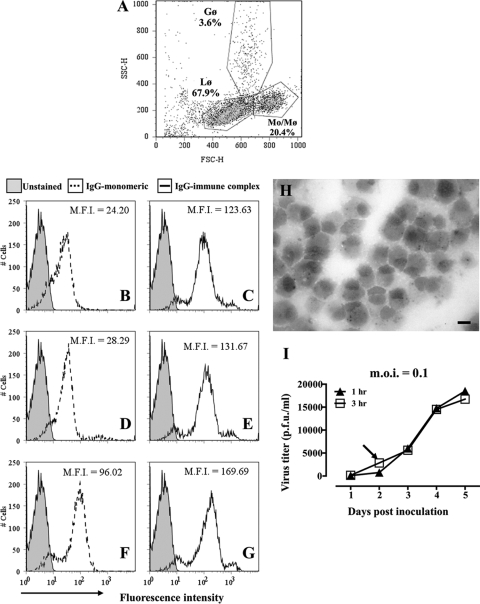
FIG. 5.
Antibody binding and WNV infection of cultured alpaca peripheral blood monocytes. (A) Flow cytometric scatter plot (forward versus side scatter) of the low-density cell fraction recovered from density gradients. Gates were set around lymphocytes (Lφ), monocytes (Mo/Mφ), and granulocytes (Gφ). The representation of each cell type within the population is indicated. (B to G) Binding of purified fluorescent alpaca IgGs to monocytes and macrophages. Leukocytes were incubated on ice with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated IgG1 (B), IgG2 (D), or IgG3 (F) alone or with HRP-conjugated goat anti-llama IgG to form immune complexes (C, E, and G). Untreated cells were used as controls. Binding of fluorochrome-labeled IgGs to cells was assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms of fluorescence intensities demonstrate the binding of IgGs to cells within the Mo/Mφ gate shown in panel A. M.F.I., mean fluorescence intensity. (H) Cytospin preparation of adherent cells from low-density fraction after 8 days in culture. Macrophages containing cytoplasmic esterase specific for α-naphthyl acetate stain black. Bar, 10 μm. (I) Macrophages (1 × 105) were incubated with WNV (MOI = 0.1) for 1 h (filled symbols) or 3 h (open symbols), washed with PBS, and cultured at 37°C for 5 days. Supernatant was sampled daily, and virus numbers were estimated by plaque assay. The arrow indicates the inoculation period (3 h) and time point of supernatant collection used in subsequent assays.