Fig. 1.
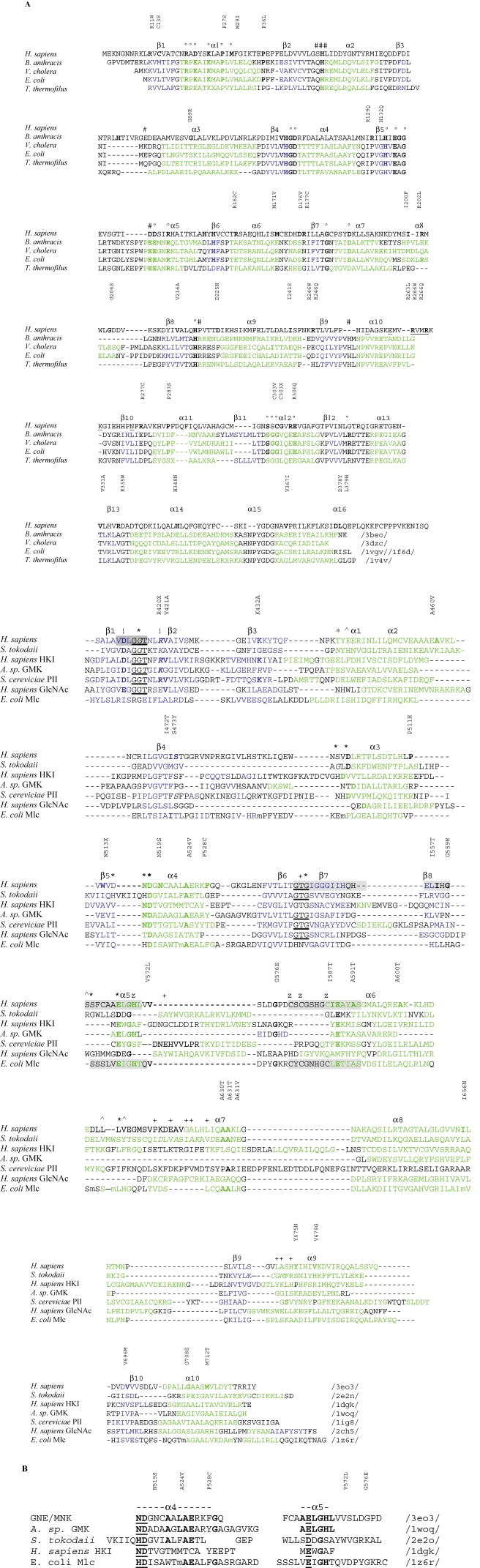
Sequence alignments of GNE/MNK. (A) Sequence alignments of mammalian and prokaryotic 2-epimerases (similar to the mammalian GNE/MNK N-terminal domain) and hexokinases (similar to the GNE/MNK C-terminal domain). Amino acids mutated in HIBM (G135, V216, R246, A631, M712, etc.), histidines, mutations of which result in loss of epimerase activity, and absolutely conserved in pro- and eukaryotic organisms ligand binding amino acids are in bold. Secondary structure assignments are shown (α-helices green and β-strands blue). For the epimerase domain, amino acids involved in allosteric regulation (#) in the B. anthracis enzyme and forming an active site (°) in the E. coli enzyme are shown in the upper line. For the kinase domain, amino acids of β1, β3α1, β4α3, β5α4, β8α5 loops involved in glucose binding (*), ADP binding (+), N-acetyl binding (^), and Mg2+ coordination (!) in S. tokodaii hexokinase /2e2o/ are shown in the upper line. Predicted allosteric site residues of the human enzyme and two phosphate binding motifs are underlined. The ATP phosphate binding motif (dark gray) and two characteristic ROK Zn2+ binding motifs (light gray) are shaded. (B) Sequence homology between parts of human GNE/MNK (upper line)/3eo3/ and the glucose binding helices of Arthrobacter sp. glucomannokinase (GMK)/1woq/, S. tokodaii hexokinase /2e2o/, and human hexokinase I (HKI)/1dgk/. Identical residues are in bold. Glucose binding residues are underlined.