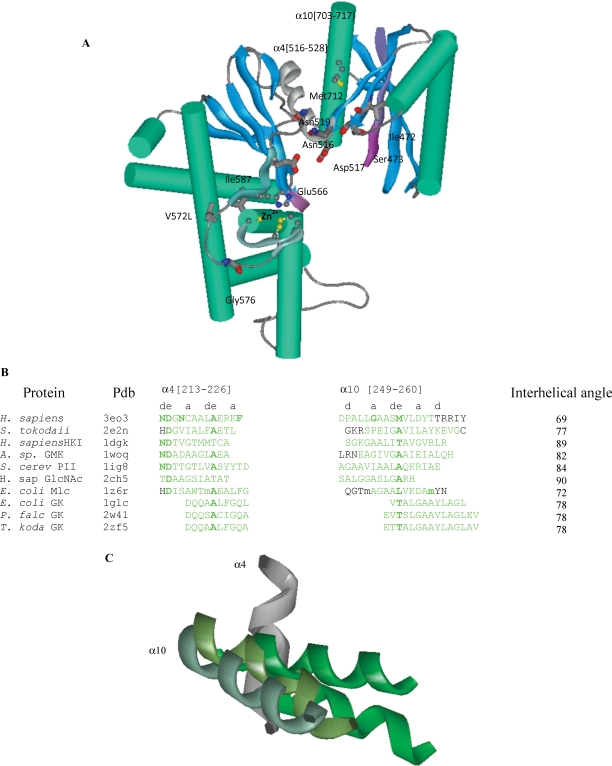
Fig. 3.
The N-acetylmannosamine kinase (MNK) domain of the human GNE/MNK protein. (A) Mutated residues Met712 at the interface of the α-helices (green) and β-sheets (blue), Asn519, Gly576, Ile587, Ile472, Ser473 and proposed glucose binding residues Asn516, Asp517, Glu566 are shown (oxygen – red, nitrogen – dark blue, carbon – gray/black, and sulfur – yellow). The two ATP binding motifs characteristic for sugar kinases are in magenta; glucose binding helices, C-terminal part of ROK1 motif and N-terminal region of ROK2 motif are gray and cyan ribbons. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the two interacting helices α4 and α10 containing GNE mutations M712T and A524V of H. sapiens MNK, S. tokodaii, H. sapiens (HKI) and S. cereviciae (PII) hexokinases, A. sp glucomannokinase, H. sapiens GlcNAc kinase and E. coli, Plasmodium falciparum and Thermococcus kodakarensis glycerol kinases. For selelomethionine, m is used. (C) Helices α4 (dark gray) and α10 (light gray) of H. sapiens MNK, S. tokodaii hexokinase, H. sapiens hexokinase, and E. coli glycerol kinases superimposed.