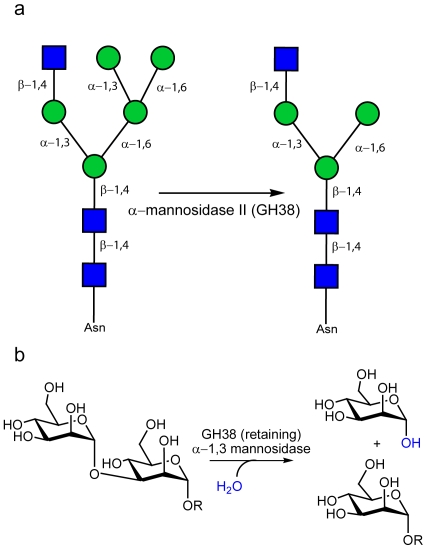
Figure 1. Catalytic activity of GH38 α−mannosidases.
(A) Golgi α−mannosidase II is responsible for the hydrolysis of both α−1,3 and α−1–6 mannosides during the diversification of hybrid N glycans (GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2 becoming GlcNAcMan3GlcNAc2). (B) The catalytic action of a retaining α−mannosidase, here exemplified for the α−1,3 mannosidase activity of GH38 enzymes; catalysis occurs with net retention of anomeric configuration.