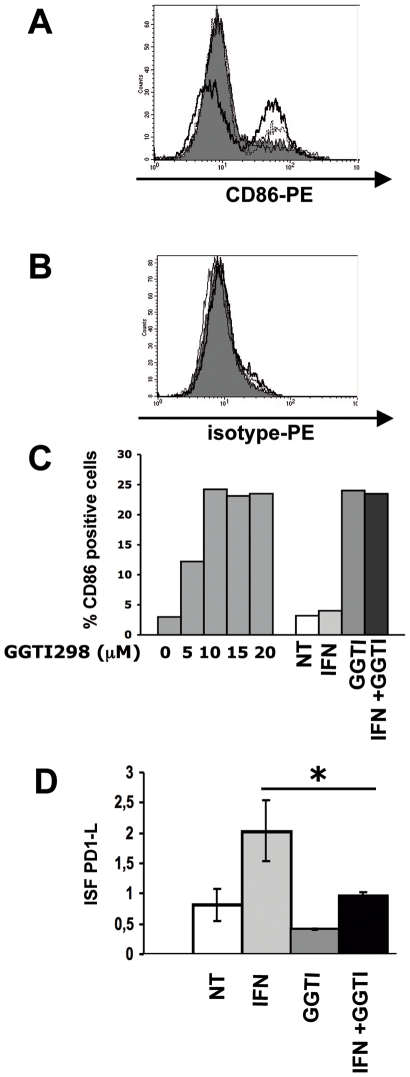
Figure 5. On LB1319-MEL cells, GGTI-298 induces enhancement of CD86 and reduction of IFN-γ-induced PD-1L expression.
Membrane expression of CD86 (A) and its isotype control (B) was determined by flow cytometry with PE-conjugated specific antibodies on LB1319-MEL cells after 4 days in vitro treatment with medium alone (filled profiles); hIFN-γ (50 IU/mL) alone (thin lines); GGTI-298 (10 µM) alone (dotted lines); or the combination of both (thick lines). Data are representative of three independent experiments. C) CD86 membrane expression was also tested by cytofluorometry on LB1319-MEL cells after 4 days treatment with either increasing doses of GGTI-298 (0, 5,10, 15 and 20 µM) or with the combination of hIFN-γ (50 IU/ml) and GGTI-298 (10 µM). Results are expressed in percentage of CD86 positive cells. D) Membrane expression of inhibitory molecule PD-1L was determined by flow cytometry with PE-conjugated specific Ab on LB1319-MEL cells after 4 days in vitro treatment with or without hIFN-γ (50 IU/ml) and/or GGTI-298 (10 µM). Results are expressed in ISF, related to isotype controls, as indicated in Material and Methods. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.