Figure 3.
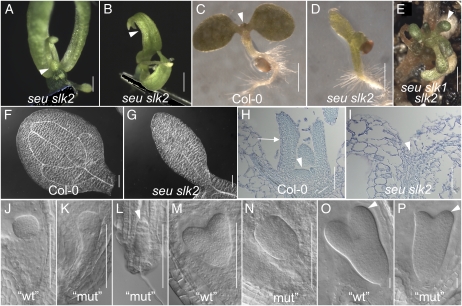
Floral, seedling, and embryonic phenotypes of seu slk2 double mutants. A, Early-arising flower from seu slk2 “escaper” plant. The arrowhead indicates a reduced gynoecial mound in whorl 4. B, Late-arising flower from seu slk2 escaper plant. The arrowhead indicates carpelloid whorl 1 sepals. C to H, Seedlings at 5 d post germination. C, Wild-type (Col-0) seedling. The arrowhead indicates leaves initiating from the SAM. D, The seu slk2 double mutant displays narrow cotyledons and a lack of true leaf development. E, A seu slk1 slk2 triple mutant seedling that has escaped embryonic lethality displays bulbous and very reduced rosette leaves (arrowhead). F, Cleared wild-type (Col-0) cotyledon shows vascular loops. G, The seu slk2 double mutant displays a very narrow cotyledon with a single unbranched central vascular element. H, Longitudinal section of a Col-0 seedling. SAM (arrowhead) and rosette leaf (arrow) are indicated. I, SAM and rosette leaves are not detected in the seu slk2 seedling. The arrowhead indicates the expected location of the SAM if wild type. J to P, Embryos segregating from a slk2/slk2 seu/+ parental self-cross. Embryos were classified as morphologically wild type (wt) or mutant (mut). See text for details. J to L, Globular-stage sibling embryos displayed wild-type (J), weakly disrupted (K), or severely disrupted (L) morphologies. The arrowhead in L indicates a globular domain with reduced cell number. M and N, Heart-stage embryos. While cotyledon primordia are apparent in morphologically wild-type embryos (M), morphologically mutant sibling embryos (N) lack obvious cotyledon primordia. O and P, Reduced cotyledon development (arrowhead) is apparent at the torpedo stage in those embryos displaying mutant morphologies (compare P with O). Bars = 100 μm in A, E, F to I, and J to N, 200 μm in B, 1 mm in C and D, and 10 μm in O and P. [See online article for color version of this figure.]