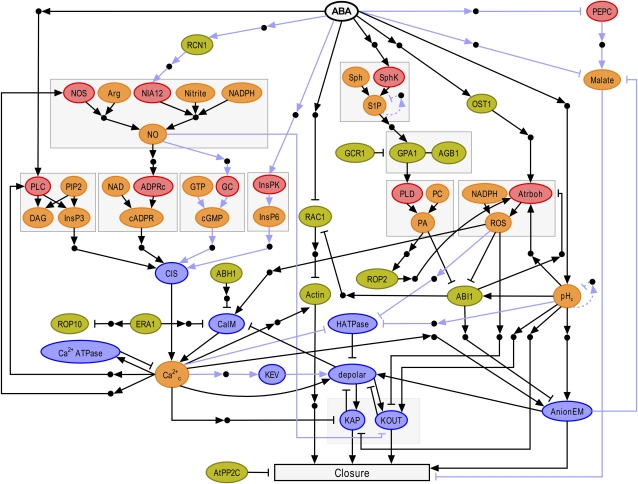
Figure 2.
Network of ABA-induced stomatal closure. (Figure and figure legend are reproduced from Li et al. [2006].) The color of each node represents its function: enzymes are shown in red, signal transduction proteins are green, membrane transport-related nodes are blue, and secondary messengers and small molecules are shown in orange. The full names of network components corresponding to each abbreviated node label are indicated below. Small black circles represent putative intermediary nodes mediating indirect regulatory interactions. Arrowheads represent activation, and short perpendicular bars indicate inhibition. Light blue lines denote interactions derived from species other than Arabidopsis, and dashed light blue lines denote inferred negative feedback loops on pH and S1P. Nodes involved in the same metabolic pathway or protein complex are bordered by gray boxes; only those arrows that point into or out of the boxes signify information flow (signal transduction). ABI1/2, Protein phosphatase 2C ABI1/2; ABH1, mRNA cap-binding protein; Actin, actin cytoskeleton reorganization; ADPRc, ADP-Rib cyclase; AGB1, heterotrimeric G protein β-subunit; AnionEM, anion efflux at the plasma membrane; AtPP2C, protein phosphatase 2C; Atrboh, NADPH oxidase; CaIM, Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane; Ca2+ ATPase, Ca2+ ATPases and Ca2+/H+ antiporters responsible for Ca2+ efflux from the cytosol; Ca2+c, cytosolic Ca2+ increase; cADPR, cyclic ADP-Rib; cGMP, cyclic GMP; CIS, Ca2+ influx to the cytosol from intracellular stores; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERA1, farnesyl transferase ERA1; GC, guanyl cyclase; GCR1, putative GPCR; GPA1, heterotrimeric G protein α-subunit; HATPase, H+-ATPase at the plasma membrane; InsPK, inositol polyphosphate kinase; InsP3, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; InsP6, inositol hexakisphosphate; KAP, K+ efflux through rapidly activating K+ channels (AP channels) at the plasma membrane; KEV, K+ efflux from the vacuole to the cytosol; KOUT, K+ efflux through slowly activating outwardly rectifying K+ channels at the plasma membrane; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; NIA12, nitrate reductase; NO, nitric oxide; OST1, protein kinase OST1; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PEPC, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; PLD, phospholipase D; RAC1, small GTPase RAC1; RCN1, protein phosphatase 2A; ROP2, small GTPase ROP2; ROP10, small GTPase ROP10; SphK, sphingosine kinase; Sph, sphingosine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate.