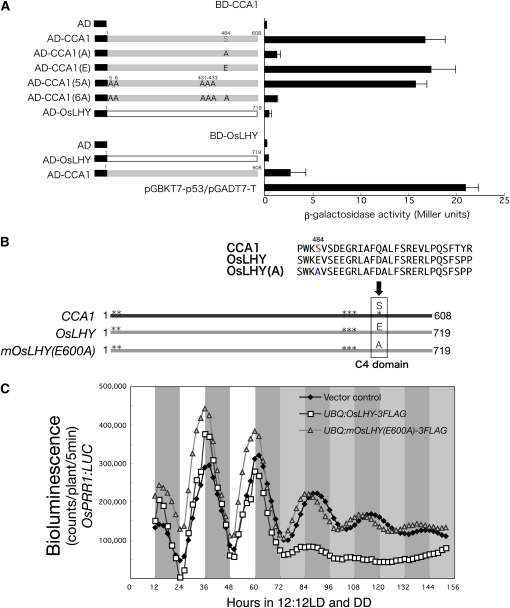
Figure 8.
Biochemical and biological roles of the Glu-600 and Ser-484 sites in OsLHY and CCA1. A, Y2H assays. Mutations in CCA1 altered the interactions with CCA1 in yeast. The Ser-484 site in CCA1 was critical for homodimer formation of CCA1 in yeast. OsLHY did not interact with OsLHY itself in yeast. All experiments were done in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions for the Matchmaker kit (BD Clontech). Average values of β-galactosidase activities from five individual colonies from a representative experiment are shown ± se at right. B, Schematic view of tested constructs with site-specific mutations. The arrow indicates the position of Glu/Ser in the C4 domain. The identified CK2 target sites are shown as asterisks for CCA1 and OsLHY. C, Bioluminescence analysis of OsPRR1:LUC expression in rice calli transformed with UBQ:mOsLHY(A)-3FLAG or UBQ:OsLHY-3FLAG in light/dark (LD) followed by constant darkness (DD) cycles. About 10 independent transformed T0 cell lines carrying the same OsPRR1:LUC reporter gene were measured. Average counts are shown.