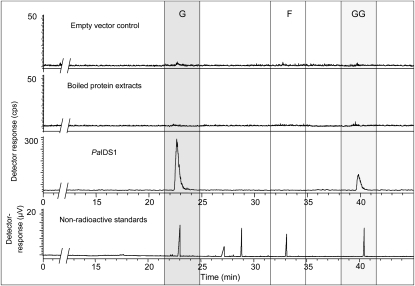
Figure 4.
Catalytic activities of recombinant PaIDS1 protein heterologously expressed in E. coli and assayed with [1-14C]IPP and DMAPP. Reaction products were hydrolyzed enzymatically, and the resulting alcohols were analyzed by radio-gas chromatography. The main hydrolysis products detected were geraniol (G) and geranylgeraniol (GG), indicating that GPP and GGPP were the principal enzyme products. No release of FPP (detected as farnesol [F]) was measured (third panel from top). The ratio of GPP to GGPP was calculated as approximately 9:1, taking into account that 1 mol of GGPP incorporates three times as much radioactivity from IPP (three units) as GPP does (one IPP unit). The substrate IPP was hydrolyzed to some extent, but the resulting isopentenol eluted close to the solvent front and is not shown. Purified protein extracts of bacteria expressing the empty vector or boiled protein extracts of bacteria expressing PaIDS1 did not show any measurable activity (two top panels). Compounds were identified by coinjection of standards, as depicted in the thermal conductivity detector trace (bottom panel). Standards included geraniol (23 min), nerol (27 min), linalool (29 min), (E,E)-farnesol (33 min), and (E,E,E)-geranylgeraniol (40.5 min). At least five different replicates of each sample were analyzed, and the variance was below 5%.