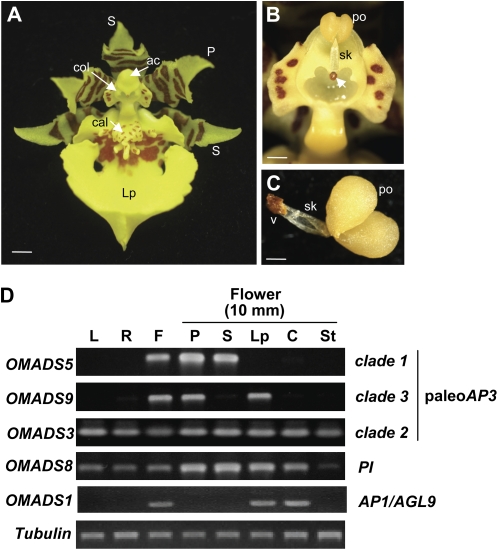
Figure 3.
Detection of expression of OMADS3, OMADS5, OMADS8, OMADS9, and OMADS1 in O. Gower Ramsey. A, An O. Gower Ramsey mature flower bud (10 mm) consisting of three sepals (S), two petals (P), a lip (Lp) with red-brown around the callus (cal), and a reproductive organs column (col). Sepals and petals are yellow with red-brown bars and blotches toward the base of the segment. ac, Anther cap. Bar = 2 mm. B, Closeup of the column. The anther cap, which covers the reproductive organs column (col in A), was removed, revealing the pollinarium (male reproductive organ), which consists of two pollinia (po), a stalk (sk), and the brown viscidium (arrowed). Bar = 0.5 mm. C, Closeup of the pollinarium. po, Pollinia; sk, stalk; v, viscidium. Bar = 0.2 mm. D, Total RNAs isolated from leaves (L), roots (R), and the flower organs sepal (S), petal (P), lip (Lp), stamen (St), and carpel (C) of 10-mm-long floral buds (F) were used as templates to detect the expression of OMADS3, OMADS5, OMADS8, and OMADS9 by RT-PCR. In this study, two pollinia, a stalk of pollinarium, and the viscidium from the column were isolated as male reproductive organs (indicated as stamen). The remaining tissues of the column were used as female reproductive organs (indicated as carpel). The results indicated that OMADS8 and OMADS3 were expressed in all four floral organs as well as in vegetative leaves and roots. The mRNA for OMADS5 was only strongly detected in sepals and petals, whereas OMADS9 was only strongly detected in petals and lips. The AGL6-like gene OMADS1 was only expressed in lips and carpels. Each experiment was repeated twice with similar results. A fragment of the α-tubulin gene was amplified as an internal control.