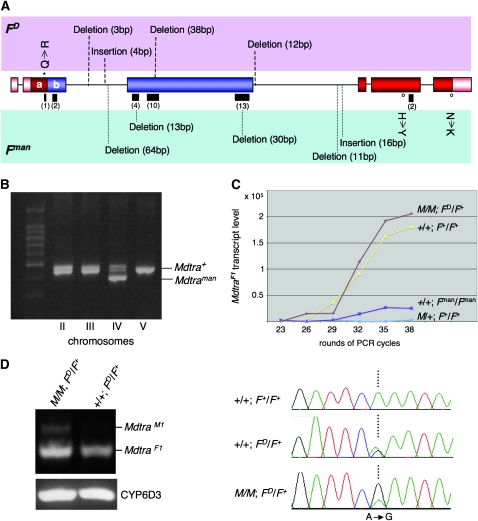
Figure 7.—
Analysis and expression of Mdtra sequences in FD and Fman mutant backgrounds. (A) Molecular lesions in the Mdtra genomic region of FD and Fman animals. The positions of insertions and deletions are indicated by either dashed lines in the FD allele (top row) or dotted lines in the Fman allele (bottom row). Lengths of insertions and deletions are given in parentheses. Amino acid substitutions are marked with an open dot for the Fman allele and with a star for the FD allele. (B) The region encompassing a 64-bp deletion in the Fman allele was amplified from flies heterozygous for one of the four marked chromosomes II, III, IV, and V (see materials and methods). Only flies heterozygous for the marker on chromosome IV also contain both the Mdtra+ and the Mdtraman allele. (C) Semiquantitative analysis of MdtraF1 transcript levels in flies of different genotypes: control males (M/+; F+/F+), No-M males (+/+; Fman/Fman), control females (+/+; F+/F+), and FD females homozygous for M (M/M; FD/F+). Total RNA was isolated from five flies per genotype and RT–PCR was performed with primer pairs Mdtra-9 and Mdtra-20. After each of the indicated cycles, 5 μl of the amplification reaction was analyzed. Intensity of the MdtraF1 bands was normalized using levels of amplified Mdtra2 products as an internal control. (D) RT–PCR of RNA from M/M; FD/F+ females detects male MdtraM1 (primers Mdtra-18 and Mdtra-3) and female MdtraF1 transcripts (primers Mdtra-18 and Mdtra-20), while RT–PCR of RNA from +/+; FD/F+ females produces only female MdtraF1 transcripts (MdCYP6D internal standard). Analysis of the sequence chromatogram of the region encompassing the MdtraD-specific nucleotide substitution A to G in exon E2a allowed us to compare the relative amounts of F+ (A) and FD (G) -derived Mdtra transcripts in the absence or the presence of M and reveals that in M/M; FD/F+ females MdtraF1 transcripts are almost exclusively derived from the FD allele. In contrast, in +/+; FD/F+ females, both F alleles produce equal amounts of MdtraF1 transcripts.