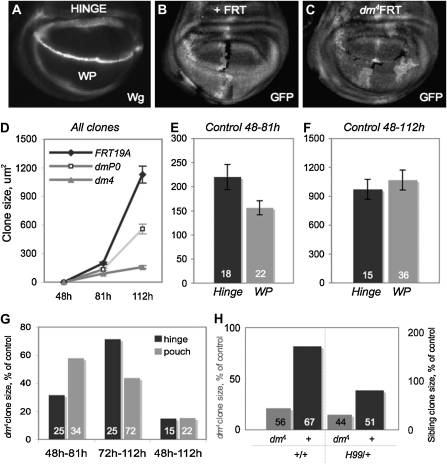
Figure 2.—
Regional and temporal growth requirements for dMyc reflect its expression pattern during wing disc growth. (A) Analysis of control and dmyc mutant clones in female larvae to determine growth requirements for dMyc. Clones were induced at specific times and scored on the basis of location: hinge (region within Wg rings) and WP (region within inner ring of Wg). Different regions of the disc were scored using either Wg or Hth staining. (B and C). Mitotic recombination produces a GFP-negative clone and a sister clone with two copies of GFP. The GFP-negative dmyc mutant clones (dmP0, hypomorphic allele, or dm4, null allele) (C) were compared to GFP-negative control clones (B). (D) Clonal growth of dmP0 mutant cells and dm4 mutant cells show a dose-dependent requirement for dmyc in cell proliferation and growth. Clones were induced at 48 hr AEL and dissected at either 81 hr AEL or 112 hr AEL to assess growth over time (where clone growth is the product of cellular growth, cell division, and cell survival). (E) Hinge cell clones grow significantly larger than WP clones early (P = 0.04). (F) WP clones later grow more to reach the same size as hinge clones by 112 hr AEL. (G) dm4 mutant clones are significantly smaller than control clones in all regions both early and late in development (P <10−3 for all dm4 mutant clones compared to corresponding control). Hinge cells are more sensitive to loss of dmyc early in development, whereas WP cells are more sensitive to loss of dmyc late in development. Early, dm4 hinge clones grow to 32% of control hinge clone size while dm4 WP clones reach 58% of control WP clone size (Mann–Whitney test, P <10−4). Later, dm4 WP clones grow to only 44% of control WP clone size while dm4 hinge clones reach 71% of control hinge clone size (Mann–Whitney test, P <10−4). By the end of development, dm4 clones in either region are <20% of corresponding control clone size. (H) Wild-type sibling clones (GFP++) of dm4 mutant clones that have grown from 48 hr AEL to 112 hr AEL are significantly bigger than corresponding control GFP++ clones (P <10−9). In a H99/+ background, wild-type sibling clones of dm4 mutant clones are no longer significantly bigger than corresponding control GFP++ clones (P = 0.17). The H99/+ background does not alter the size of the dm4 mutant clone (combined from all regions: P = 0.83). Bar graphs are labeled with number of clones measured.