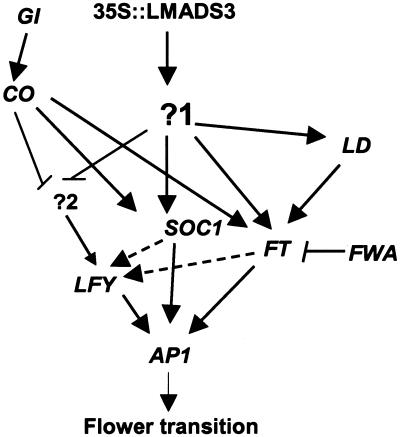
Figure 8.
Possible model for the affect caused by 35S::LMADS3 in transgenic Arabidopsis. Ectopic expression of LMADS3 promoted flowering by activating (→) an unknown gene (?1) and caused indirect activation of flowering time genes FT, SOC1, and LD and floral meristem identity genes such as LFY and AP1 during early development. Ectopic expression of LMADS3 may also cause the suppression (→) of a pathway (?2) involved in the activation (→) of LFY during floral initiation. This pathway was also possibly suppressed (→) by the 35S::CO as described by Onouchi et al. (2000). On the basis of this model, LFY activity will be abolished in ft-1 or fwa-1 mutants ectopically expressing LMADS3 and results in the formation of leaf-like flowers as seen in our results.