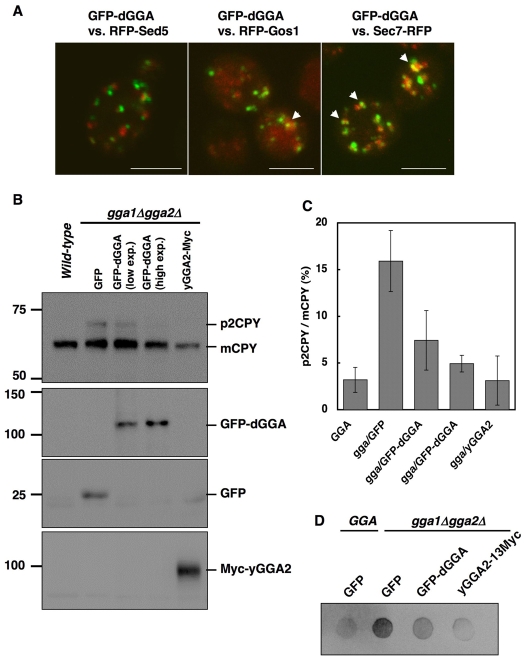
Fig. 8.
Functional complementation of the vps phenotype of gga-deficient yeast by overexpression of dGGA. (A) Distribution of EGFP-dGGA in the yeast. Wild-type (SEY6210) cells were co-transformed with EGFP-dGGA and mRFP-coupled Sed5 (cis-Golgi, left panel), Gos1 (medial-Golgi, center panel) or Sec7 (trans-Golgi, right panel) expression vectors. Confocal images from four slices with 1-μm interval in depth were projected for each panel. Colocalized foci are indicated with arrows. Scale bars: 5 μm. (B) Wild-type or gga1Δgga2Δ double disruptant (GPY2385) cells were transformed with plasmids for expression of EGFP, EGFP-dGGA or yeast GGA2-13Myc. EGFP-dGGA expression was also induced with 0.5 mM CuSO4 for 8 hours (high exp.). The transformants were harvested and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-CPY antibody. (C) Quantification of the CPY processing. The ratio of the intensity of p2CPY to that of mCPY was plotted. The value indicate mean ± s.d. (D) CPY secretion assay. Cells growing in mid-log phase were spotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane placed on a growth plate. After incubation overnight, cells were washed out and the membrane was subjected to immunoblotting for CPY.