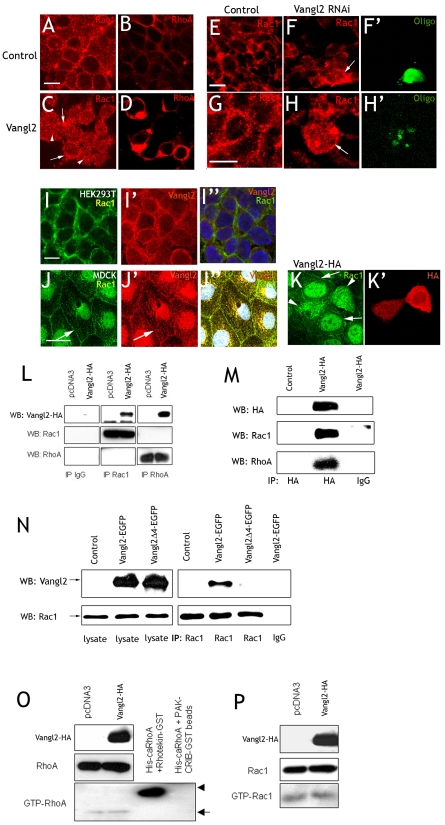
Fig. 2.
Vangl2 binds and redistributes Rac1. (A-I″) HEK293T cells. (A) The cell membranes of control cells display a distinct punctuate Rac1 labeling. (C) Vangl2-transfected cells display strong labeling of Rac1 in the membrane (arrows), and increased cytoplasmic labeling (arrowheads). (B,D) Vangl2 increases RhoA labeling intensity in the cell cortex (B) compared to control cells (D). (E,G,F,H) Rac1 in control and Vangl2 RNAi knockdown cells. (F,H) Vangl2 RNAi knockdown results in a more diffuse cortical Rac1 labeling and increased cytoplasmic labeling. Transfection in F and H is verified with a control oligo (F′,H′). (I-I″) Rac1 (I′) and endogenous Vangl2 (I′) overlap (I″) in the cortex of untreated HEK293T cells. (J-K′) MDCK cells. Rac1 (arrow in J) and Vangl2 (arrow in J′) overlap in the cell membranes of control transfected cells. (J″) Merged picture including DAPI. (K,K′) Cells overexpressing Vangl2-HA (K′, arrowheads in K) display a diffuse, cytoplasmic Rac1 distribution. Adjacent, untransfected cells display distinct Rac1 labeling in the cell membranes (arrows in K). (L-N) Lysates from cells transfected with Vangl2-HA, Vangl2-EGFP or Vangl2Δ4-EGFP were immunoprecipitated as indicated with anti-Rac1, anti-RhoA or anti-HA, and used for western blots with anti-HA, anti-Rac1 or anti-RhoA. (L,M) Distinct bands of the correct size demonstrate that Rac1 and RhoA are part of the same protein complex as Vangl2. (N) Rac1 immunoprecipitates Vangl2-GFP, but not Vangl2Δ4-EGFP. (O,P) Despite the ability of Vangl2 to bind Rac1 and RhoA, pull-down assays shows that the activities of RhoA (O) and Rac1 (P) are not affected by Vangl2. Scale bars: 10 μm.