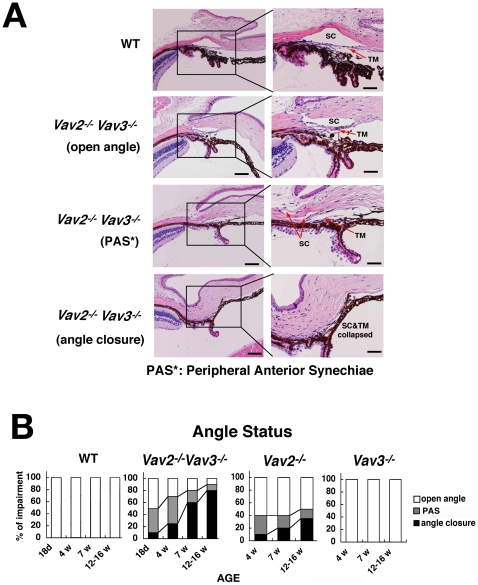
Figure 4. Characterization of progressive iridocorneal angle closures in Vav2−/−Vav3 −/− and Vav2 −/− mice.
The aqueous humor outflow facility, trabecular meshwork (TM) and Schlemm's canal (SC) (iridocornial angle) in Vav2/Vav3-deficient (Vav2−/−Vav3 −/−) mice are evaluated in histological manner. Vav2-deficient (Vav2 −/−) mice also have the same changes, but of lower severity. A. Representative photos of normal TM and SC histology of 12-week-old wild-type (WT) mice as a control. Representative photos of normal open angle, peripheral anterior synechiae (PAS) in 12-week-old Vav2−/−Vav3 −/− mice, and angle closure status in 12-week-old Vav2−/−Vav3 −/− mice. Sections used here are all representative from 20 samples. Scale bars: left photos, 200 µm; right photos, 100 µm. B. Changes of angle status appear at the early ages. We classify angle status of Vav2−/−Vav3 −/−, Vav2 −/−, and Vav3 −/−mice into open angle, PAS, and angle closure by histological evaluation. We find the changes of angle status at the early ages, such as in 18-day-old Vav2−/−Vav3−/− mice (n = 20) and in 4-week-old of Vav2−/−Vav3−/− mice (n = 20). We took four (Vav2 −/− Vav3 −/−) and three (Vav2 −/−, Vav3 −/−) different age groups, with 20 mice examined, respectively.