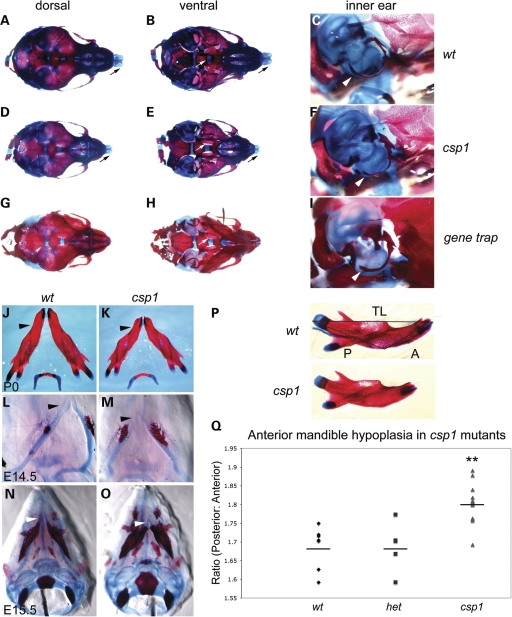
Figure 2.
csp1 and Prdm16Gt683Lex mutants exhibit craniofacial skeleton defects with anterior-specific mandibular hypoplasia. (A–I) Abnormalities in the craniofacial skeleton in newborn csp1 mutants are evident in dorsal (A, D and G) and ventral (B, E and H) views of Alcian blue/Alazarin-stained heads. In addition, hypoplasia of the mutant tympanic rings is evident (C, F and I). Newborn mutants show failure of palatine bone fusion (white arrows in B, E and H), variably shortened frontonasal region (D and G) and abnormal nasal cartilage formation (black arrows in A, B, D and E) and shortening and abnormal curvature of the anterior mandible (black arrowheads in J and K). Anterior shortening of Meckel's cartilage is evident early during craniofacial bone formation at E14.5 (L and M) and E15.5 (N and O). In addition, csp1 mutant mandibles appear smaller than wild-type counterparts, and ossification appears to be more robust. Morphometric analysis using measurements of the posterior (P in P) and anterior (A in P) aspects of newborn csp1 (n = 14), heterozygous (n = 5) and wild-type (n = 7) mandible bones, followed by calculation of the posterior:anterior (P/A) ratios, detects an anterior-specific mandibular hypoplasia (Q). P/A ratios were significantly greater in csp1 mutants (mean: 1.802, standard deviation: 0.050) compared with wild-type (mean: 1.687, standard deviation: 0.056) and heterozygous pups (mean: 1.688, standard deviation: 0.066) using ANOVA (P < 0.0001). In the chart (Q), the double asterisk designates statistical significance, and horizontal lines denote the means for each genotype class.