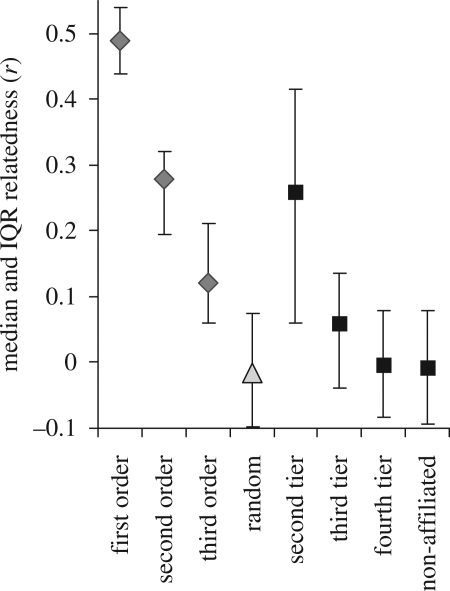
Figure 4.
Average pair-wise relatedness values for the three social tiers analysed are compared with average relatedness values from known first-, second- and third-order relatives (i.e. mother–calf, half sibling and first cousins). Relatedness declines rapidly up the social hierarchy, from approximately the level of second order (half siblings) among second-tier group members to levels no different than random among fourth-tier group associates. Interestingly, relatedness values from randomly selected and unaffiliated pairs were not distinguishable from levels calculated for fourth-tier associates, showing the latter are not genetically based.