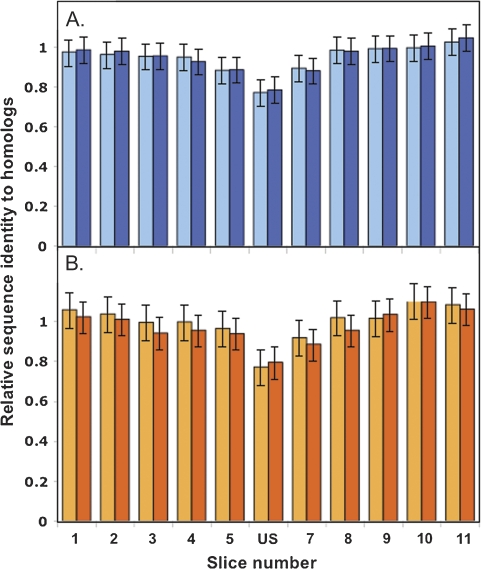
FIG. 5.—
Peptide sequence identity as a function of distance from the uptake sequence position for US-containing genes with three comparison homologs (see table 3). Each protein was aligned with its three homologs, and the 99-aa region centered on the US-encoded peptide was divided into 11 9-aa slices. The mean pairwise percent identity of the three query–homolog pairs and three homolog–homolog pairs was determined for each slice and was normalized by the corresponding value for the overall trimmed alignment of each protein to its 3 homologs. Error bars are 95% confidence limits from a one-way analysis of variance. (A) Average identities for slices of 131 H. influenzae sequences aligned to homologs: mean of three query–homolog comparisons (light blue); mean of three homolog–homolog comparisons (dark blue). (B) Average identities for slices of 86 N. meningitidis sequences aligned to homologs: mean of three query–homolog comparisons (light orange); mean of 3 homolog–homolog comparisons (dark orange).