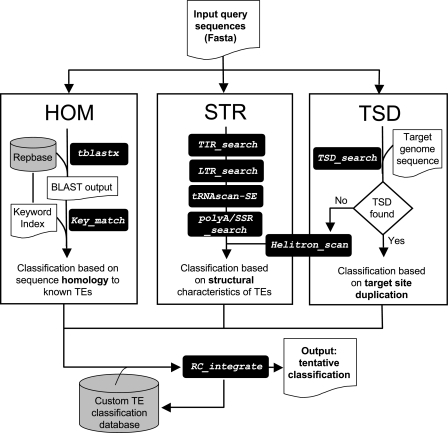
FIG. 1.—
Overview of the REPCLASS workflow. Subroutines are shown in italics in black boxes. Databases are shown in gray cylinders. Each input query sequence (typically a consensus) is analyzed by the three classification modules of REPCLASS. HOM: homology-based, searches similarity to known repeats deposited in Repbase using TBlastX and extract classification from keyword index file; STR: structure-based, several subroutines search for structural features characteristic of different group of TEs, such as terminal inverted repeats (TIR_search), LTRs (LTR_search), tRNA-like sequences (tRNAscan-SE), or polyA/SSRs (polyA/SSR_search); TSD: target site duplication, individual copies are extracted from the target genome sequence using BlastN and their flanking sequences are searched for TSD. If no TSD are found, the subroutine Helitron_scan is executed to look for structural features of Helitrons. The final step attempts to compare and integrate the results of the three modules, resulting in a tentative classification for each input sequence. For a complete description of the workflow and subroutines, see Results and Methods.