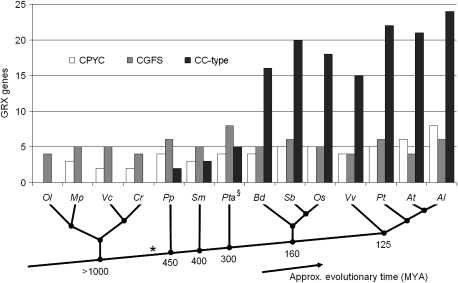
FIG. 1.—
The sizes of the three classes of GRXs in green algae and plants. Although CPYC and CGFS GRXs are present in all organisms including green algae, CC-type GRXs have only been observed in land plants. The first CC-type gene is likely to have arisen 1,000–450 Ma (*), and in angiosperms, their numbers have increased dramatically in comparison to CPYC and CGFS GRXs. (§) Denotes the use of EST library sequencing, and as such, more GRX genes might exist in the Pinus genome. Abbreviations: Ol, Ostreococcus lucimarinus; Mp, Micromonas pusilla; Vc, Volvox carteri; Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Pp, Physcomitrella patens; Sm, Selaginella moellendorffii, Pta, Pinus taeda; Bd, Brachypodium distachyon; Sb, Sorghum bicolor, Os, Oryza sativa; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; At, A. thaliana; and Al, A. lyrata. The emergence of the bryophytes has been estimated at 450 Ma (Lang et al. 2008; Rensing et al. 2008). The divergence of lycophytes is estimated at 400 Ma, with the first distinctive lycophyte fossil dated at ∼345 Ma (Banks 2008). The gymnosperms are estimated to have diverged from angiosperms some 300 Ma (Theissen and Becker 2004). The divergence of monocots and eudicots has been estimated to be 140–150 Ma (Chaw et al. 2004). The divergence of the Vitales (Vitis) from the rosids (Arabidopsis/Populus) occurred approximately 125 Ma (Wikstrom et al. 2001).