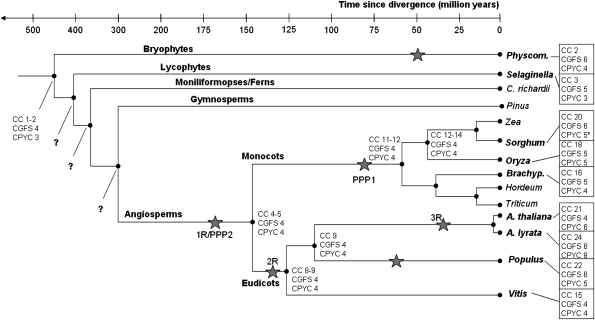
FIG. 5.—
The expansion of CC-type GRX class compared with the CPYC and CGFS classes in land plants. The predicted number of genes in the last common ancestor was estimated by orthologous clustering and is given at each node. Genome duplications denoted by stars are mentioned in the following articles (Simillion et al. 2002; Maere et al. 2005; Zhang et al. 2005; Rensing et al. 2008). (*) Denotes the omission of the Sorghum CPYC-like gene (SbGRX32), which might be a pseudogene. Abbreviations: CC, CC-type GRX; Physcom., Physcomitrella; C. richardii, Ceratopteris richardii; and Brachyp., Brachypodium. The origin of the ferns is estimated to have occurred ∼365 Ma (Pryer et al. 2004). The Zea mays/Sorghum/Oryza lineage diverged from the Brachypodium/Hordeum/Triticum lineage approximately 50–60 Ma (Paterson et al. 2003), the Zea/Sorghum lineage diverged from the Oryza lineage ∼42 Ma (Paterson et al. 2003), and the Zea lineage diverged from Sorghum 10–14 Ma (Gaut et al. 1996). The Brachypodium lineage diverged from the Hordeum/Triticum lineage 35–40 Ma (Bossolini et al. 2007), and the Hordeum lineage diverged from the Triticum lineage ∼12 Ma (Wolfe et al. 1989). The divergence of Populus from Arabidopsis occurred 100–120 Ma (Tuskan et al. 2006). Divergence of A. thaliana and A. lyrata is estimated at 3.0–5.8 Ma (Clauss and Koch 2006).