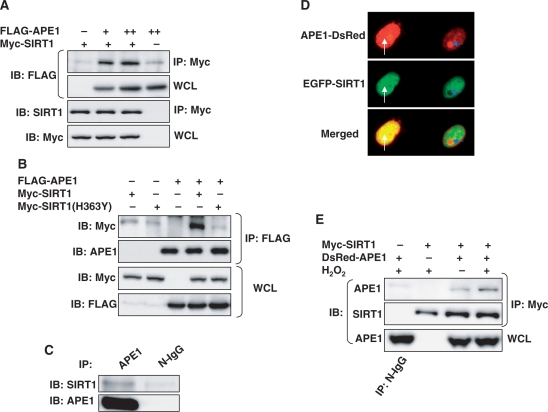
Figure 1.
APE1 and SIRT1 associate with each other. (A) APE1 and SIRT1 bind to each other in HEK 293 cells. Immunoprecipitation of epitope-tagged SIRT1 co-precipitates epitope-tagged APE1 expressed in HEK 293 cells. (B) APE1 does not bind to catalytically inactive dominant negative SIRT1. Immunoprecipitation of epitope-tagged APE1 co-precipitates epitope-tagged wild-type SIRT1 but not dominant negative SIRT1 (H363Y) expressed in HEK 293 cells. (C) Endogenous SIRT1 binds to endogenous APE1. Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous SIRT1 and APE1 in HEK 293 cells. (D) Co-localization of fluorescent epitope-tagged SIRT1 and APE1 expressed in HEK 293 cells. Co-localization of extra-nucleolar (white arrow) APE1 but not nucleolar (blue arrow) APE1 with SIRT1 is shown. (E) Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) promotes binding of APE1 to SIRT1. H2O2 (500 µM, 30 min) increases co-precipitation of epitope-tagged SIRT1 in immunoprecipitates of epitope-tagged APE1 expressed in HEK 293 cells. WCL: whole cell lysate. N-IgG: non-immune immunoglobulin. FLAG-APE1 and Myc-SIRT1 were expressed in A and B, DsRed-APE1 and EGFP-SIRT1 in C, and DsRed-APE1 and Myc-SIRT1 in D.