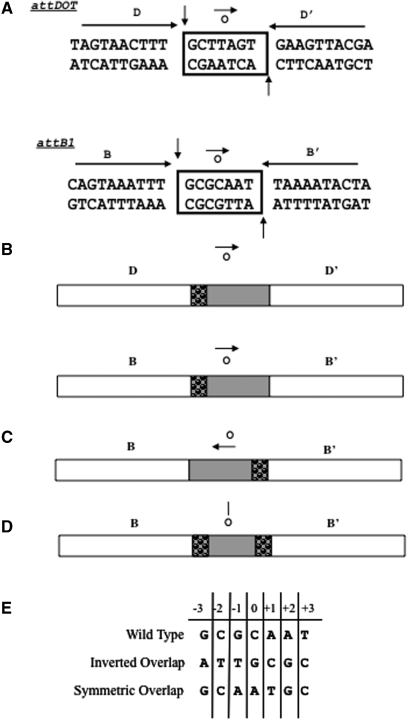
Figure 1.
(A) Wild-type sequences of the core-binding sites attDOT and attB. The boxed region indicates the overlap region (o). The conserved GC dinucleotide is shown at the left sides of the overlap regions. The remaining bases in the overlap are the coupling sequences that vary from site to site. The small arrow represents orientation of the overlap region relative to flanking arm sites. The longer arrows indicate the imperfect inverted repeats that flank the overlap regions. The D and B sites contain 8 of 10 identical base pairs. The vertical arrows show the sites of cleavage on the top and bottom strands. (B) Simplified schematic diagram of the same core regions. The bubbled area denotes the GC dinucleotide homology between the attDOT and attB1 overlap regions. (C) Schematic diagram of the attB site with an inverted overlap region. The arrow denotes the directionality of the overlap sequence. (D) Schematic diagram of the attB site containing a symmetric overlap region. The line over the ‘o’ represents a line of symmetry within the overlap region. (E) Sequences of the wild type, inverted and symmetric overlap regions.