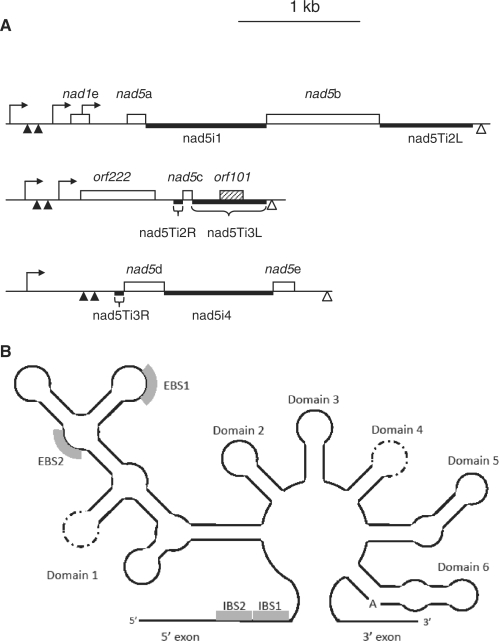
Figure 1.
Organization and expression of B. napus nad5 exons and introns. (A) Introns are designated according to (20). Open boxes indicate exons, the shaded box the open reading frame within nad5Ti3L. Thick lines indicate predicted functional domains of introns. Transcription initiation sites are indicated as hooked arrows, 5′ processing sites as filled triangles and 3′ termini as open triangles. The L and R designations are used to refer to the 5′ and 3′ portions, respectively, of the trans-splicing introns nad5Ti2 and nad5Ti3. (B) Simplified schematic of a generalized group II intron, illustrating the various structural domains. EBS and IBS stand for exon and intron binding sites, respectively, as patterned on (42). The perforated lines indicate the domain loop sites at which the RNA is disjoined in trans-plicing introns of all flowering plants (Domain 4) and further disjoined in the Oenothera nad5 Ti3L intron (Domain 1). Thus, what is a continuous RNA in cis-splicing introns is discontinuous in trans-splicing introns; in the latter case the domain stem is thought to form through base-paring interactions between two distinct RNAs.