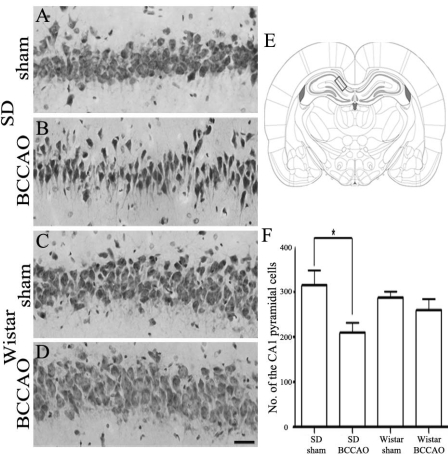
Fig. 3.
Cresyl violet staining of the hippocampal CA1 damage after 21 days of bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO). Hippocampal CA1 lesion of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats subjected to sham operation (A) or BCCAO (B). Hippocampal CA1 region of Wistar rats subjected to sham operation (C) or BCCAO (D). Schematic representation of the rat hippocampal CA1 region (E, adapted from Paxinos and Watson, 2007). The rectangle indicates the area of the brain that was examined in this study. The number of cells in the hippocampal CA1 region in SD and Wistar rats subjected to sham operation or BCCAO (F). Note that BCCAO induced significantly more pyramidal neuronal damage in CA1 subfield of the hippocampus of SD rats than in that of Wistar rats. There was no difference in the number of CA1 pyramidal neurons between sham-operated and BCCAO-induced Wistar rats. The data shown are the mean number of intact pyramidal neurons (±SD). Scale bar in A-D = 50 µm. *p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA.