Figure 5.
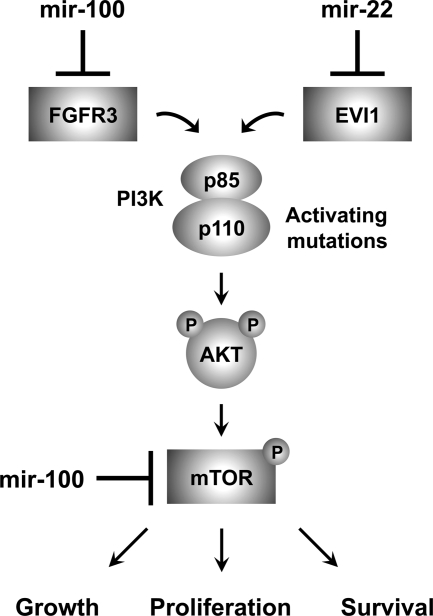
mir-100 and mir-22 target known oncogenes that influence the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. PI3K is comprised of the p85 regulatory subunit (PIK3R1) and the p110 catalytic subunit (PIK3CA). PI3K activation leads to the synthesis of the second messenger PIP3, which recruits AKT to the cell membrane for subsequent phosphorylation and activation. AKT activation has multiple biological consequences including the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, and survival by activating a key downstream effector, the serine/threonine kinase mTOR. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is frequently activated in clear cell ovarian cancer, usually secondary to gain of function mutations in PIK3CA. We found that mTOR was up-regulated in clear cell ovarian cancer cell lines and repressed by mir-100 on the mRNA and protein levels. mir-100 overexpression also decreased levels of the phosphorylated isoforms of 4EBP1 and p70 S6 kinase, two direct substrates of mTOR kinase activity that mediate mTOR signaling. Two other target oncogenes that were overexpressed in clear cell ovarian cancer also impinge on this pathway. Signaling through FGFRs, such as the mir-100 target FGFR3, induces recruitment and activation of PI3K, and the mir-22 target EVI1 promotes cell survival by stimulating PI3K/AKT signaling. Thus, mir-100 and mir-22 exert tumor suppressor activity through the coordinated repression of multiple components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.