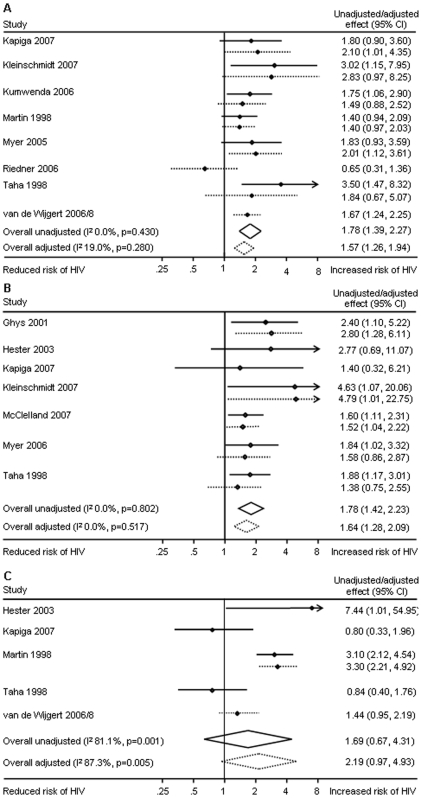
Figure 4. Meta-analyses of studies reporting associations between vaginal infections and HIV, unadjusted and adjusted effect estimates.
Panel A: Bacterial vaginosis is associated with incident HIV infection. Eight studies contribute to the pooled adjusted effect estimate with little between study heterogeneity. Panel B: Trichomonas vaginalis infection is associated with incident HIV infection. Five studies contribute to the pooled adjusted effect estimate with no between study heterogeneity. Panel C: Candida or other yeast infections are not consistently associated with incident HIV infection. Two studies, with differing results contribute to the pooled adjusted effect estimate. Minor differences between effect estimates in the table and those in published papers are possible.