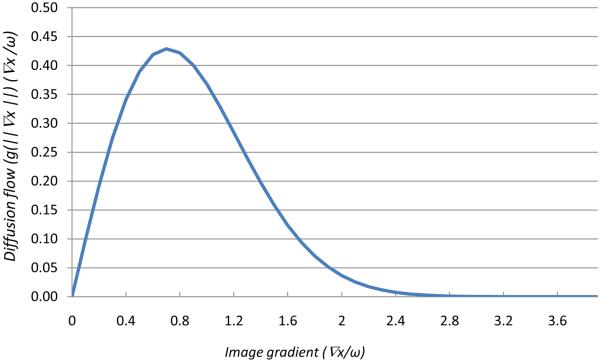
Fig.1.
Mechanism of a diffusion filter for removing noise and preserving edges. Diffusion flow (Y-axis) is plotted as a function of image gradients (X-axis). When the gradient ∇I is close to zero (homogeneity regions) or when the flow is much greater than k (the edges), the flow rapidly decreases to zero which indicates no filtering processing. This implies that the diffusion filter processing maintains a homogeneous region and preserves edge information. The flow is maximum when the gradient strength is near to the diffusion constant k. To reduce noise in the image, k is carefully chosen so that the flow is maximum and the filter will remove the noise at that gradient.