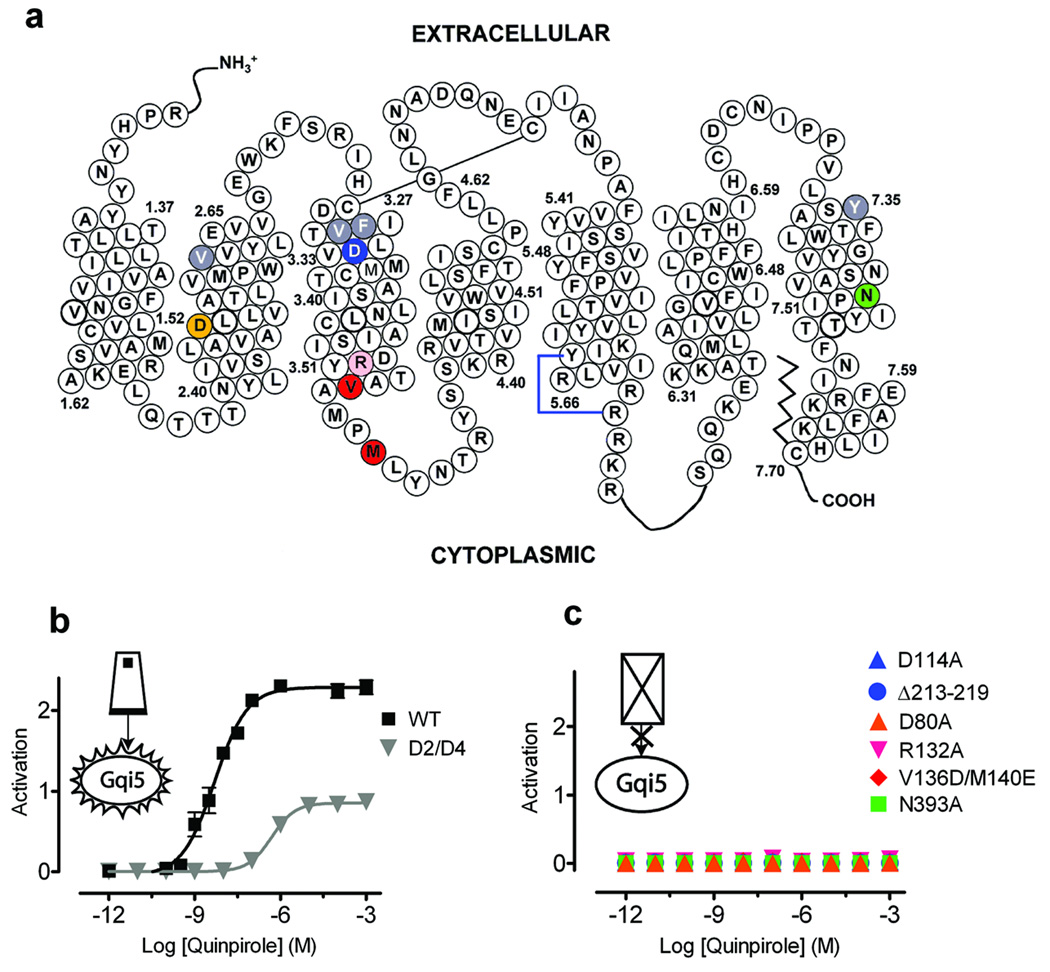
Figure 2. Characterization of D2R mutants.
(a) Schematic representation showing the positions of the mutations in the D2 receptor, with coloring corresponding to the symbols and lines in (b) and (c). (b) D2/D4, a D2 mutant with 4 amino acids substituted from the D4 receptor (V912.61F/F1103.29L/V1113.28M/Y4087.35V) making it 1000-times more sensitive to a D4-selective inhibitor (Supplementary Fig. 4 online), is activated by quinpirole, albeit with a lower potency and efficacy when compared with WT D2R. (c) All the other mutants, which are described in the text, were non-functional. Activation data were normalized as in Fig. 1. The mean±SEM of at least 3 experiments, each conducted in triplicate, are shown.