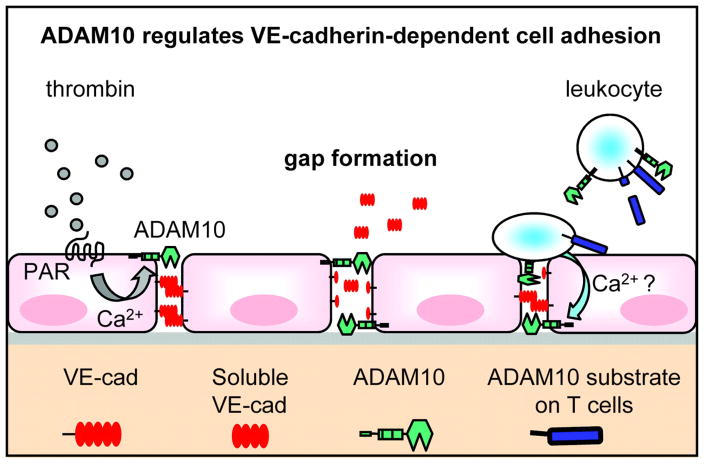
Figure 6. Schematic model of ADAM10-dependent endothelial gap formation.
Thrombin binding to its receptor (PAR-1) induces intracellular signaling pathways, which activate ADAM10-dependent VE-cadherin proteolysis. This effect contributes to endothelial cell dissociation and gap formation. ADAM10 also regulates the transmigration of T cells through the endothelium. Most likely, the binding of activated T cells to the endothelium induces intracellular signaling cascades in endothelial cells, which lead to ADAM10 activation and increased VE-cadherin proteolysis. T cell-expressed ADAM10 might also contribute to the regulation of the transmigration process through cleavage of cell adhesion molecules on the T cell surface or through trans-shedding of endothelial VE-cadherin.