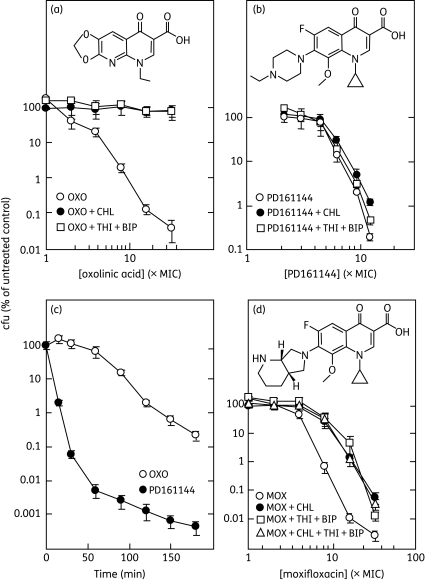
Figure 1.
Effect of thiourea plus 2,2′-bipyridyl and chloramphenicol on quinolone lethality. Exponentially growing E. coli cultures were treated with either chloramphenicol or thiourea plus 2,2′-bipyridyl for 10 min, and then quinolone was added. After incubation, the percentage survival was determined as described in the text. (a) Oxolinic acid (OXO). Oxolinic acid alone (MIC = 0.25 mg/L), with 20 mg/L chloramphenicol (CHL; MIC = 2 mg/L) or with 100 mM thiourea (THI; MIC = 200 mM) plus 0.25 mM 2,2′-bipyridyl (BIP; MIC = 0.5 mM) was added at the indicated concentrations to strain SD104 (KD447) followed by incubation for 120 min. (b) PD161144. As in (a) except that PD161144 (MIC = 0.08 mg/L) replaced oxolinic acid and the incubation time was 45 min. (c) Rate of quinolone-mediated killing. Strain SD104 was treated with oxolinic acid or PD161144 at 10× the MIC for the indicated times, after which percentage survival was determined. (d) Moxifloxacin (MOX). Strain SD104 was treated with moxifloxacin (MIC = 0.06 mg/L) for 45 min, with or without pre-treatment as in (a). In addition, cells were pre-treated with chloramphenicol and thiourea plus 2,2′-bipyridyl for 10 min. Error bars represent standard deviations from the mean; similar results were obtained in replicate experiments.