Abstract
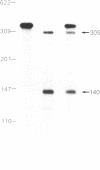
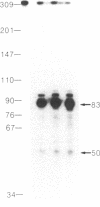
The high-affinity IgE receptor present on mast cells and basophils is responsible for the IgE-mediated activation of these cells. The current model for this receptor depicts a four-subunit structure, alpha beta gamma 2. A cDNA for the alpha subunit was recently cloned and predicts a structure consisting of two homologous extracellular domains, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic tail. Using a synthetic oligonucleotide corresponding to the amino-terminal sequence of the alpha subunit, we identified a number of cDNA clones from a rat basophilic leukemia cell cDNA library. Nucleotide sequencing established four different forms of cDNA: one is nearly identical to the published cDNA; the second differs from the first in the 5' untranslated sequence; the other two forms use either one or the other of the 5'-end sequences as above and lack 163 base pairs in the region coding for the second extracellular domain. RNase protection analysis with radioactive RNA probes established the heterogeneity of rat basophilic leukemia cell mRNA with regard to both the 5' and the internal sequences. Our results suggest the existence of at least four different protein forms related to the alpha subunit of the high-affinity IgE receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitcher D. L., Mostov K. E. Alternate splicing of rabbit polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2712–2715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froese A. Structure and function of the receptor for IgE. Crit Rev Immunol. 1980 May;1(2):79–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Walker I. D., Kirszbaum L., Pietersz G. A., Deacon N. J., Chambers G. W., McKenzie I. F., Hogarth P. M. The murine Fc receptor for immunoglobulin: purification, partial amino acid sequence, and isolation of cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6980–6984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K. Activation of mast cells for mediator release through IgE receptors. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:188–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinet J. P., Metzger H., Hakimi J., Kochan J. A cDNA presumptively coding for the alpha subunit of the receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4605–4610. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Isersky C., Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. I. Evidence for specific binding of IgE. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):600–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. A., Koch T., Plutner H., Mellman I. A complementary DNA clone for a macrophage-lymphocyte Fc receptor. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):372–375. doi: 10.1038/324372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Orida N. Synthesis of surface immunoglobulin E receptor in Xenopus oocytes by translation of mRNA from rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10649–10652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H., Alcaraz G., Hohman R., Kinet J. P., Pribluda V., Quarto R. The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:419–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecoud A. R., Ruddy S., Conrad D. H. Functional and partial chemical characterization of the carbohydrate moieties of the IgE receptor on rat basophilic leukemia cells and rat mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1624–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Raney P., Halvorson H. O. Cytoplasmic and secreted Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase mRNAs encoded by one gene can be differentially or coordinately regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1682–1688. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Luster A. D., Weinshank R., Kochan J., Pavlovec A., Portnoy D. A., Hulmes J., Pan Y. C., Unkeless J. C. Structural heterogeneity and functional domains of murine immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2946078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivnay B., Rossi G., Henkart M., Metzger H. Reconstitution of the receptor for immunoglobulin E into liposomes. Reincorporation of purified receptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1212–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Austen K. F. Structure and function of the chemical mediators of mast cells. Prog Allergy. 1984;34:271–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Tepler I., Benfey P. N., Berenstein E. H., Siraganian R. P., Leder P. Human and rat mast cell high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptors: characterization of putative alpha-chain gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]