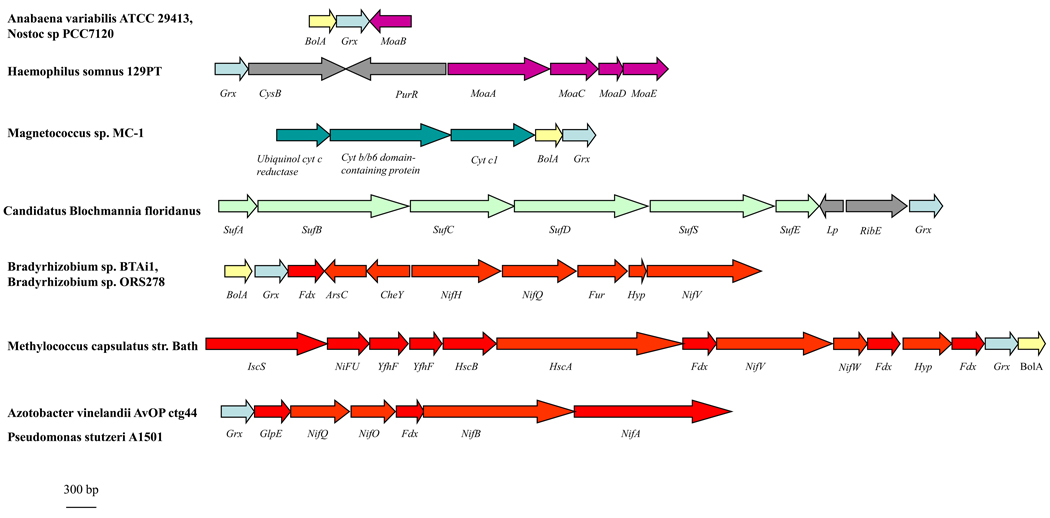
Figure 5. Gene clustering between CGFS Grx-encoding genes and iron- or molybdenum-related genes.
Based on the genome analysis of approximately 2500 sequenced microorganisms available using the “protein clusters” tool available at the NCBI webpage and the Microbial Genome Database (MGDB, http://mbgd.genome.ad.jp/), we list genes involved in metal homeostasis which are either directly adjacent to CGFS Grx-encoding genes or belong to a putative operon containing a CGFS Grx gene. The size of the genes is drawn to scale. Hyp stands for genes which encode hypothetical proteins, CysB codes for a LysR-type transcriptional regulator, PurR for the master regulatory protein of purine nucleotide biosynthesis, Lp for lipoprotein, RibE for the subunit alpha of a flavin synthase, ArsC for an arsenate reductase of the C-type, CheY for a transcriptional regulatory protein, Fdx for a ferredoxin, Fur for the ferric uptake regulator and GlpE for a protein of the rhodanese/sulphurtransferase family. MoaA, B, C, D, E encode proteins belonging to the molybdenum biosynthetic pathway, SufA, B, C, D, E, S and NifA, B, H, Q, O, U, V, W encode proteins belonging to the SUF and NIF assembly machinery, respectively. IscS encode a cysteine desulphurase, Yfhf a scaffold proteins and HscA and B encode two chaperone proteins.