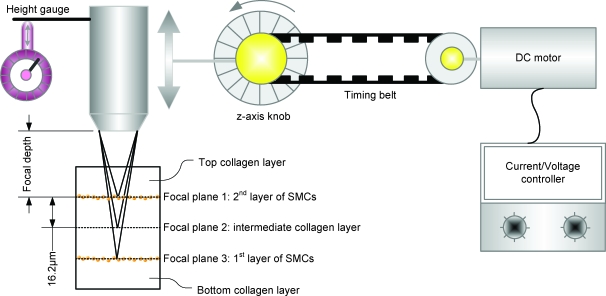
FIG. 5.
Focal 3D imaging method using a motorized microscope. A direct current motor was connected to control the z-axis knob of a fluorescence microscope body by a timing belt. Each image was taken at a scheduled time by a charge-coupled device camera control software. The distance of each layer was calculated by the reference index of the microscope (65 μm/360°), motor speed (180°/s), and imaging time control (0.5 s/image). These conditions gave a resolution of 16.2 μm separation between each image for an 81-μm thick patch (five layers). Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/ten.