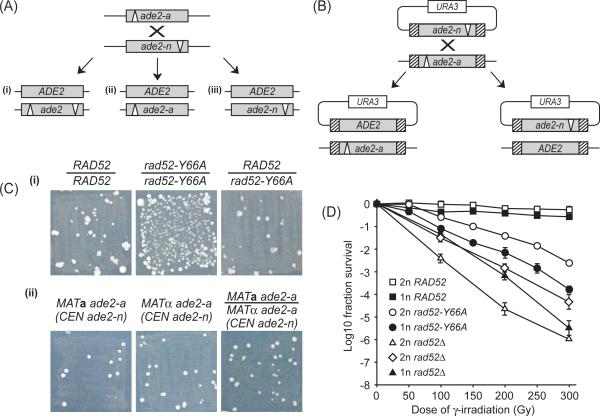
Fig. 1.
Heteroallelic recombination and DNA repair. (A) Assay for interchromosomal recombination between the ade2-a and ade2-n heteroalleles in diploid cells. -a and -n denote the deletion of the AatII and NdeI enzyme restriction sites, respectively. Three outcomes resulting in adenine prototrophs are illustrated: (i) reciprocal exchange, (ii) conversion of the ade-n allele, and (iii) conversion of the ade2-a allele. (B) Spontaneous recombination between heteroalleles located at the endogenous ADE2 locus (ade2-a) and on a single-copy plasmid (ade2-n). (C) Genomic context of heteroallelic recombination. Patches of prototroph recombinants after replica plating onto SC-Ade plates. (i) MATa RAD52 ade2-a/MATα RAD52 ade2-n, MATa rad52-Y66A ade2-a/MATα rad52-Y66A ade2-n, and MATa RAD52 ade2-a/MATα rad52-Y66A ade2-n diploid strains. (ii) MATa rad52-Y66A ade2-a haploid, MATα rad52-Y66A ade2-a haploid, and MATa rad52-Y66A ade2-a/MATα rad52-Y66A ade2-a transformed with single-copy plasmid carrying the ade2-n heteroallele. (D) Survival after γ-irradiation. Haploid (1n) and diploid (2n) strains were analyzed by counting colonies of surviving cells after 3 days unless otherwise stated. □ RAD52 diploid; ■ RAD52 haploid; ◯ rad52-Y66A diploid; ● rad52-Y66A haploid; △ rad52 null (rad52Δ) diploid; ◇ rad52 null (rad52Δ) diploid after 6 days; and ▲ rad52 null (rad52Δ) haploid. In the rad52 null diploid after 6 days many survivors exhibit loss of the TRP1, LYS2 and/or MAT markers either independently or in combination, indicating that >60% of the survivors are aneuploid (2n-1, 2n-2 and 2n-3), whereas <5% of wild-type survivors are aneuploid. Curves represent the average of 3 trials and error-bars indicate the standard error of the mean.