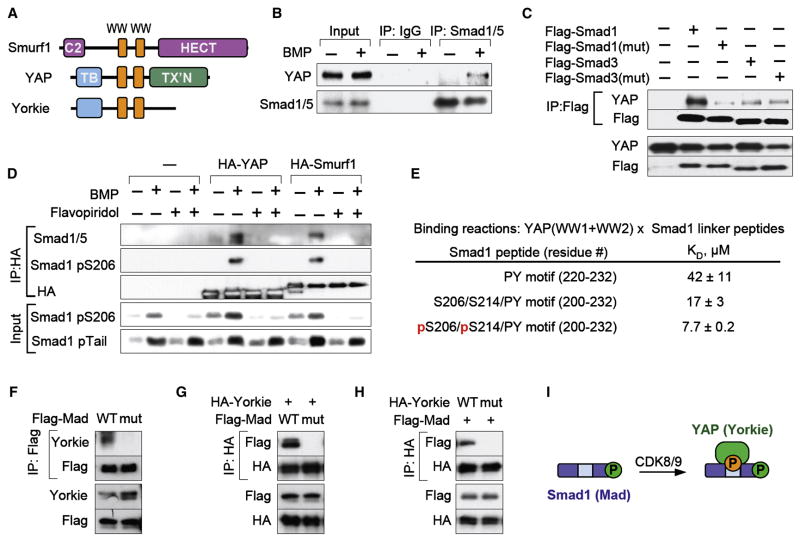
Figure 6. Smad1 linker phosphorylation mediates binding of YAP.
(A) Schematic representation of Smurf1 and YAP. Orange boxes, WW domains; C2, calcium and lipid binding domain; HECT, ubiquitin ligase domain; TB, TEAD bindng domain, TX’N, transcription activation domain. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous YAP and Smad1 in BMP-treated HaCaT cells. Complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting. (C) HEK293T cells transfected with vectors encoding Flag-tagged Smad1 or Smad3 (wild-type or linker mutant) were subjected to Flag immunoprecipitation and analyzed by immunoblotting. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with vectors encoding HA-tagged YAP or Smurf1 and after BMP stimulation in the presence or absence of flavopiridol, HA immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated anti-Smad1 antibodies. (E) Dissociation constants of the interaction of a YAP (WW1+WW2) protein fragment with the indicated Smad1 linker peptides, as measured by isothermal titration calorimetry. (F) Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with Flag-Mad wild-type or linker mutant and Flag-immunoprecipitates were tested for the presence of endogenous Yorkie by immunoblot. (G) As in (E), with cotransfection of HA-Yorkie and immunoprecipitation of the HA-species. (H) As in (F), with transfection and immunoprecipitation of wild-type or WW domain mutant Yorkie. (I) Schematic representation of the recruitment of YAP upon CDK8/9-mediated linker phosphorylation of Smad1.