Fig. 4A.
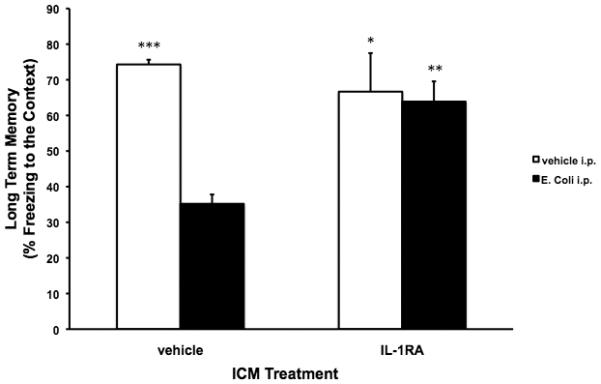
Exogenous IL-1RA blocked the E. coli-induced LTM impairments in 24 mo animals. 24 mo animals were injected ICM with either vehicle or IL-1RA. Immediately following ICM injection, animals were injected i.p. with either vehicle or E. coli. 4 d post-injections, all animals underwent contextual fear conditioning. 3 d post-conditioning, all animals were given a LTM test for the context. In vehicle ICM treated animals, E. coli treatment resulted in a significant impairment of LTM (% freezing to the context) compared to vehicle ICM/vehicle i.p. (*** p < .001), IL-1RA ICM/vehicle i.p. (* p < .05), and IL-1RA ICM/E. coli i.p. (** p < .01) groups. IL-1RA treatment completely blocked the E. coli-induced impairment in LTM resulting in LTM similar to the vehicle ICM/vehicle i.p. and IL-1RA ICM/vehicle i.p. groups. N = 4 animals/group.
