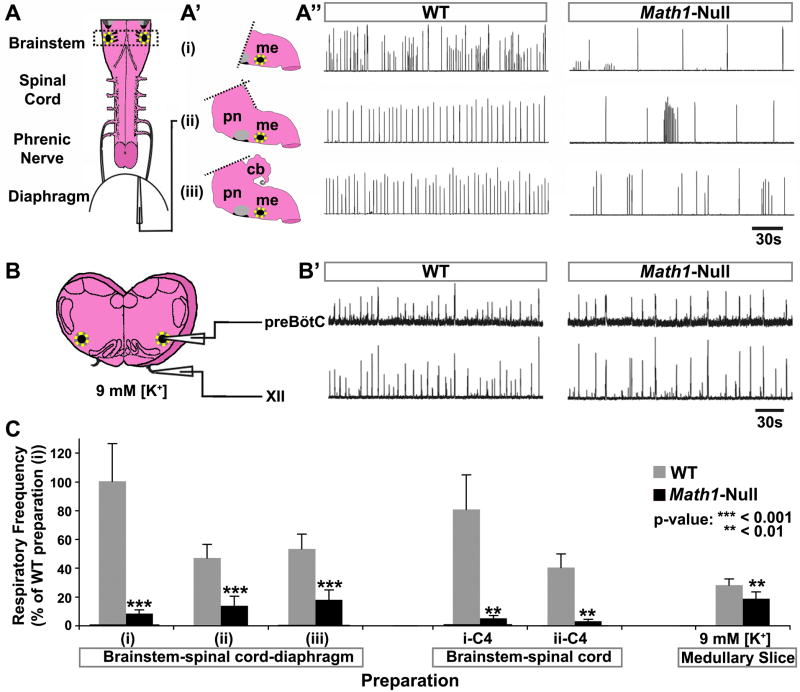
Figure 1. Math1-Null Mice Die after Birth because of Too-Slow Central Respiratory Rhythm.
(A) Schematic of the standard brainstem-spinal cord-diaphragm (BSD) preparation used for respiratory physiology (includes only the medullary portion of the brainstem). (A′) Schematics depicting three variations of the BSD preparation in which different portions of the brainstem were included: (i) medulla only, (ii) pons and medulla, and (iii) cerebellum, pons, and medulla. (A″) Rectified and integrated suction electrode recordings from the diaphragm muscle EMG in the three BSD preparations from E18.5 WT mice (left column) and Math1-null mice (right column). The rhythm was significantly slower and more irregular in all Math1-null preparations. Yellow dotted circle on each schematic indicates the preBötC, while the black region ventral to the facial nucleus (gray circle) represents the pFRG/RTN.
(B) Schematic of medullary slice preparation containing the preBötC (from the region indicated by the dashed rectangle in (A)). (B′) Rectified and integrated suction electrode recordings from the preBötC (top) and XII motoneuron pool (bottom) of WT (left) and Math1-null (right) slice preparations (in 9mM [K+]). The frequency was again slower in Math1-null preparations but was more stable than in the BSD preparations.
(C) Population data of respiratory frequency from WT (gray) and Math1-null (black) mice for each BSD preparation (i–iii) depicted in (A), for recordings directly from C4 in these preparations after removal of the diaphragm (i-C4: medulla only, ii-C4: pons and medulla), and for the medullary slice preparations. Data was normalized to that of WT preparation (i) for ease of comparison. P-values indicate a significant difference between Math1-null and WT tissue within each preparation. See Table S1 for frequency, sample size, and statistical analyses. Abbreviations: cerebellum (cb), hypoglossal motor nucleus (XII), medulla (me), pons (pn), pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC).