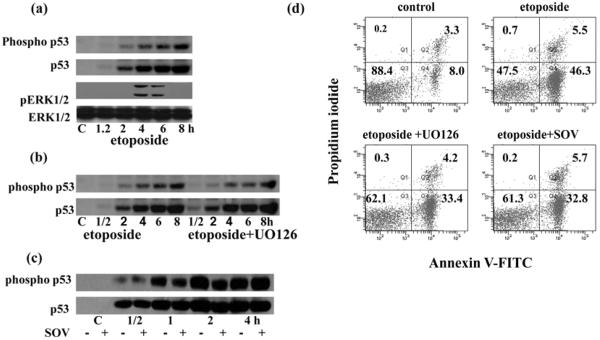
Figure 7. DNA damage induced both p53 and ERK1/2 activation as well as apoptosis.
(a) Thymocytes were treated with 100μM etoposide. Total and phosphorylated p53 and total and phosphorylated ERK1/2 were determined by immunoblotting. Phosphorylation and stabilization of p53 was also determined in etoposide treated thymocytes with or without 1 hour UO126 (10μM) pretreatment (b) and with or without 1 hour sodium orthovanadate (100μM) pretreatment (c). Representative blots from three experiments are shown in each (a), (b) and (c).
(d) Apoptosis of thymocytes was determined after etoposide treatment in the presence or absence of UO126 or sodium orthovanadate. UO126 (10μM) and sodium orthovanadate (100μM) were added for 1 hour before addition of etoposide (100 μM). Cells were maintained in the presence of etoposide for 4 hours. Cells were stained after the different treatments with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide following the manufactures instructions and analyzed by flow cytometry on a LSR II or FACSAria using BD FACS Diva software (BD Bioscience). Data represent one of five different experiments with similar results.