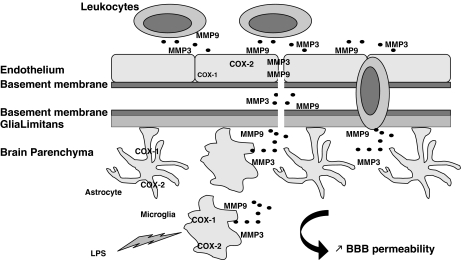
Figure 5.
Distinct effects of COX-1 and -2 deletion on LPS-induced BBB disruption. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activates primarily microglia, which releases cytokines, chemokines, MMP-9, and MMP-3. The neuroinflammatory response, through chemokines and cytokines, also propagates to the surrounding cells such as astrocytes and endothelial cells. Chemokines initiate signals that lead to leukocyte arrest, adhesion, and extravasation through the endothelium and perivascular space. The action of MMP-9 and MMP-3, released by activated microglia and leukocytes, allow leukocyte entry into the brain parenchyma by attacking the basement membrane and glia limitans. Although present in all cell types, COX-1 is mainly found in microglia, and COX-2 is predominant in neurons and endothelial cells. COX-1 deletion decreases chemokine expression and MMP-3 activity, which most likely will attenuate LPS-induced increase in BBB permeability. However, COX-2 deletion exacerbates LPS-induced BBB disruption, through an increase in chemokine release and MMP-9 and MMP-3 activities.