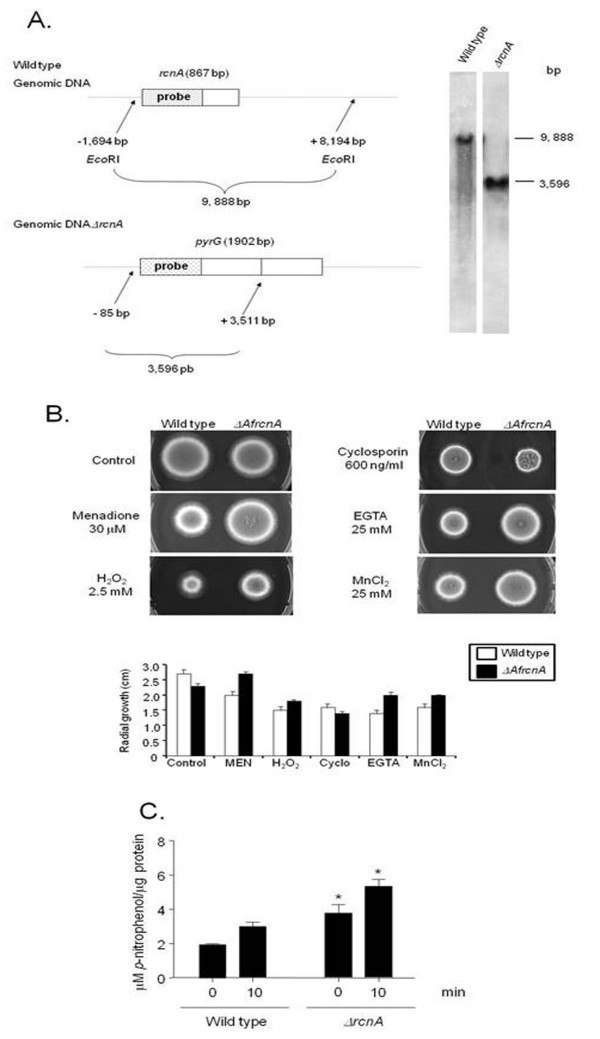
Figure 4.
Molecular characterization of the A. fumigatus AfrcnA. (A) Schematic illustration of the rcnA deletion strategy. (A) Genomic DNA from both wild type and ΔAfrcnA strains was isolated and cleaved with the enzyme EcoRI; a 2.0-kb DNA fragment from the 5'-noncoding region was used as a hybridization probe. This fragment recognizes a single DNA band (about 9.8-kb) in the wild type strain and also a single DNA band (about 3.6-kb) in the ΔrcnA mutant as shown in the Southern blot analysis. (B) Wild type and ΔAfrcnA mutant strains were grown for 72 hours at 37°C in complete medium in the absence or presence of menadione 30 μM, H2O2 2.5 mM, cyclosporine A 600 ng/ml, EGTA 25 mM, and MnCl2 25 mM. The graph shows the radial growth (cm) of the strains under different growth conditions. The results are the means ± standard deviation of four sets of experiments. (C) Wild type and ΔrcnA mutant strains were grown in YG medium for 16 hours at 37°C and then exposed to 200 mM CaCl2 for 10 minutes. Mycelial protein extracts were processed and calcineurin activity measured. Asterisks indicate the ΔrcnA samples are significantly different from the wild type strain (p < 0.05).