Fig. 3.
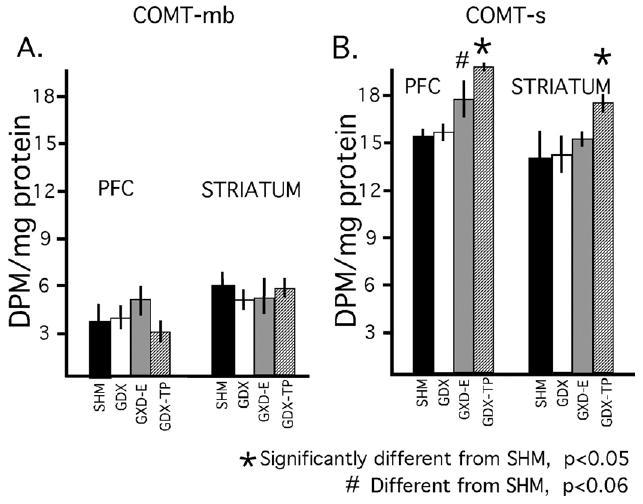
Bar graphs showing the mean (±standard error of the mean), protein normalized activities for the membrane-bound and soluble isoforms of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT-mb, COMT-s) in prefrontal cortex (PFC) and striatal tissue dissected from animals that were sham-operated (SHM, black bars), gonadectomized (GDX, white bars), gonadectomized and supplemented with estradiol (GDX-E, gray bars) or gonadectomized and supplemented with testosterone propionate (GDX-TP, stippled bars) for 28 days. There were no obvious effects of hormone deprivation or hormone replacement on the brain-abundant membrane bound isoform of COMT (A). There were also no obvious effects of gonadectomy on cortical or subcortical activity of COMT-s (B). There were, however, significant effects of hormone replacement of gonadectomized rats with testosterone propionate in cortical and striatal tissue, and near significant effects of hormone replacement of gonadectomized rats with estradiol in prefrontal cortex.
