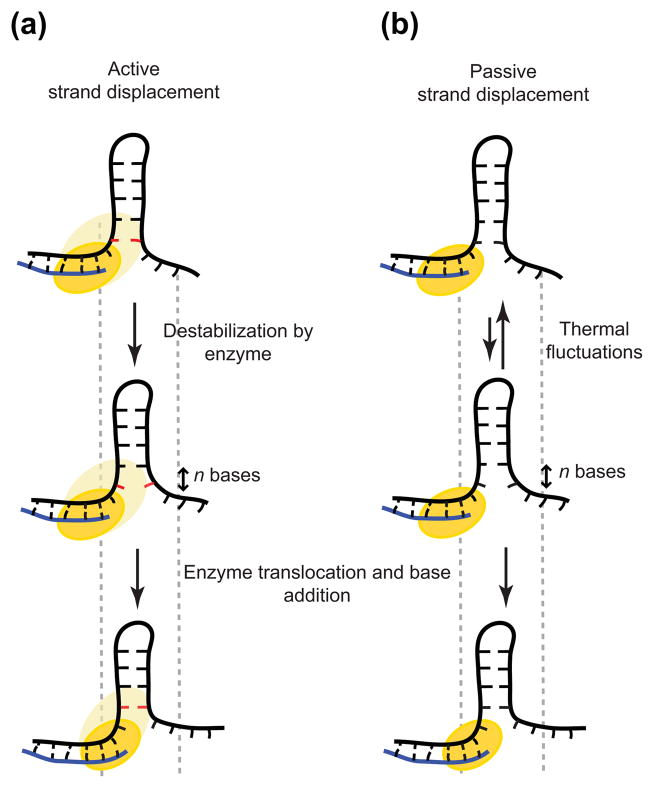
Figure 4. Active and passive mechanisms for strand displacement DNA synthesis by HIV-1 RT near hairpin locations.
(a) Active strand displacement. Yellow imprint demonstrates the interaction between the enzyme and DNA, which destabilizes DNA junction (red base). (b) Passive strand displacement. The enzyme waits for junction opening by thermal fluctuations. In both cases, n bases are the number of bases open in front of the enzyme in each turnover of strand displacement synthesis.